LOC401317, a p53-regulated long non-coding RNA, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2
- PMID: 25422887
- PMCID: PMC4244030
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110674
LOC401317, a p53-regulated long non-coding RNA, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2
Abstract
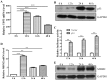
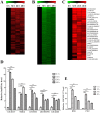
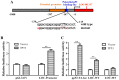
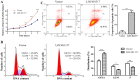
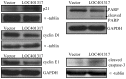
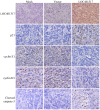
Recent studies have revealed that long non-coding RNAs participate in all steps of cancer initiation and progression by regulating protein-coding genes at the epigenetic, transcriptional, and post-transcriptional levels. Long non-coding RNAs are in turn regulated by other genes, forming a complex regulatory network. The regulation networks between the p53 tumor suppressor and these RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma remains unclear. The aims of this study were to investigate the regulatory roles of the TP53 gene in regulating long non-coding RNA expression profiles and to study the function of a TP53-regulated long non-coding RNA (LOC401317) in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE2. Long non-coding RNA expression profiling indicated that 133 long non-coding RNAs were upregulated in the human NPC cell line HNE2 cells following TP53 overexpression, while 1057 were downregulated. Among these aberrantly expressed long non-coding RNAs, LOC401317 was the most significantly upregulated one. Further studies indicated that LOC401317 is directly regulated by p53 and that ectopic expression of LOC401317 inhibits HNE2 cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. LOC401317 inhibited cell cycle progression by increasing p21 expression and decreasing cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 expression and promoted apoptosis through the induction of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and caspase-3 cleavage. Collectively, these results suggest that LOC401317 is directly regulated by p53 and exerts antitumor effects in HNE2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Guigay J (2008) Advances in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol 20:264–269. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang W, Xiang B, Zhou M, et al. (2011) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: advances in genomics and molecular genetics. Sci China Life Sci 54:966–975. - PubMed
-
- Liao Q, Zeng Z, Guo X, Li X, Wei F, et al. (2014) LPLUNC1 suppresses IL-6-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via inhibiting the Stat3 activation. Oncogene 33:2098–2109. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Huang H, Huang L, Sun M, Yan Q, et al. (2014) Regulation network and expression profiles of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs and their potential target host genes in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Sci China Life Sci 57:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

