High-speed ultrahigh-resolution OCT of Bruch's membrane in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type 2
- PMID: 25423645
- PMCID: PMC4712916
- DOI: 10.3928/23258160-20141118-20
High-speed ultrahigh-resolution OCT of Bruch's membrane in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type 2
Abstract
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) type 2 is characterized by electron-dense deposits in the glomerular basement membrane and drusen-like deposits in Bruch's membrane. Over time, atrophic changes in the retina and retinal pigment epithelium occur, which can progress to choroidal neovascularization (CNV). This report describes a patient with MPGN type 2 who developed progressive loss of vision secondary to CNV. High-speed ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography (UHR-OCT) showed an irregular Bruch's membrane that measured 10 μm beneath the foveal center. High-speed UHR-OCT can potentially be used to analyze Bruch's membrane in secondary ocular manifestations of diseases such as MPGN type 2 and primary retinal diseases such as age-related macular degeneration.
Copyright 2014, SLACK Incorporated.
Figures

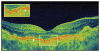
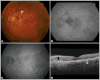

Similar articles
-
Multimodal imaging of retinal pigment epithelial detachments in patients with C3 glomerulopathy: case report and review of the literature.BMC Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov 22;17(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12886-017-0602-4. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29166869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fundus changes in type III membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: a case report.BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Mar 6;18(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-0738-x. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29510686 Free PMC article.
-
[Ocular impairment during type II membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2002 Nov;25(9):949-54. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2002. PMID: 12515943 French.
-
High-resolution optical coherence tomography of subpigment epithelial structures in patients with pigment epithelium detachment secondary to age-related macular degeneration.Br J Ophthalmol. 2012 Aug;96(8):1088-91. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301415. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22694959
-
[Drusen in Bruch's membrane. Their significance for the pathogenesis and therapy of age-associated macular degeneration].Ophthalmologe. 1992 Oct;89(5):363-86. Ophthalmologe. 1992. PMID: 1304217 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Multimodal imaging of retinal pigment epithelial detachments in patients with C3 glomerulopathy: case report and review of the literature.BMC Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov 22;17(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12886-017-0602-4. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29166869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Retinal Complications of C3 Dense Deposit Disease: A Scoping Review.Vision (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;9(3):64. doi: 10.3390/vision9030064. Vision (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40843788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpretation of anatomic correlates of outer retinal bands in optical coherence tomography.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Oct;246(20):2140-2150. doi: 10.1177/15353702211022674. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34111984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloudy Cornea with Arcus Juvenilis in a Case of Dense Deposit Disease.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Jun 27;2018:bcr2018224545. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224545. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29950499 Free PMC article.
-
Polarization-resolved analysis of outer retinal bands: investigating ballistic and multiply scattered photons using full-field swept-source optical coherence tomography.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Jul 18;15(8):4749-4763. doi: 10.1364/BOE.523202. eCollection 2024 Aug 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 39346986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McAvoy CE, Silvestri G. Retinal changes associated with type 2 glomerulonephritis. Eye. 2005;19(9):985–989. - PubMed
-
- D’Souza YB, Jones CJ, Short CD, Roberts IS, Bonshek RE. Oligosaccharide composition is similar in drusen and dense deposits in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II. Kidney Int. 2009;75(8):824–827. - PubMed
-
- Ritter M, Bolz M, Haidinger M, et al. Functional and morphological macular abnormalities in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010;94(8):1112–1114. - PubMed
-
- Dense deposit disease in children: prognostic value of clinical and pathologic indicators. The Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985;6(3):161–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

