The Hippo pathway as a target of the Drosophila DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory pathway
- PMID: 25424907
- PMCID: PMC4244634
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07196
The Hippo pathway as a target of the Drosophila DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory pathway
Abstract
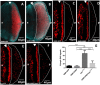
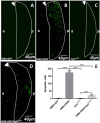
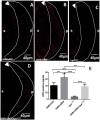
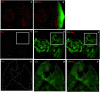
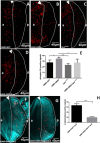
The DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory system has been demonstrated to activate a wide variety of genes with various functions. In Drosophila, the Hippo pathway is known to suppress cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through inactivation of Yorkie, a transcription co-activator. In the present study, we found that half dose reduction of the hippo (hpo) gene induces ectopic DNA synthesis in eye discs that is suppressed by overexpression of DREF. Half reduction of the hpo gene dose reduced apoptosis in DREF-overexpressing flies. Consistent with these observations, overexpression of DREF increased the levels of hpo and phosphorylated Yorkie in eye discs. Interestingly, the diap1-lacZ reporter was seen to be significantly decreased by overexpression of DREF. Luciferase reporter assays in cultured S2 cells revealed that one of two DREs identified in the hpo gene promoter region was responsible for promoter activity in S2 cells. Furthermore, endogenous hpo mRNA was reduced in DREF knockdown S2 cells, and chromatin immnunoprecipitation assays with anti-DREF antibodies proved that DREF binds specifically to the hpo gene promoter region containing DREs in vivo. Together, these results indicate that the DRE/DREF pathway is required for transcriptional activation of the hpo gene to positively control Hippo pathways.
Figures





References
-
- Hirose F., Yamaguchi M., Handa H., Inomata Y. & Matsukage A. Novel 8-base pair sequence (Drosophila DNA replication-related element) and specific binding factor involved in the expression of Drosophila genes for DNA polymerase alpha and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 2092–2099 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Matsukage A., Hirose F., Yoo M. A. & Yamaguchi M. The DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory system: a master key for cell proliferation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1779, 81–89, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.11.011 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y. & Matsukage A. Essential role of E2F recognition sites in regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene promoter during Drosophila development. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25159–25165 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Okudaira K. et al. Transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila orc2 gene by the DREF pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1732, 23–30, 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.10.009 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

