Cooperation of DLC1 and CDK6 affects breast cancer clinical outcome
- PMID: 25425654
- PMCID: PMC4291472
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.114.014894
Cooperation of DLC1 and CDK6 affects breast cancer clinical outcome
Abstract
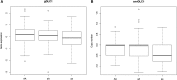
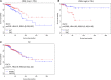
Low DLC1 expression is found to frequently co-occur with aberrant expression of cell cycle genes including CDK6 in human lung and colon cancer. Here, we explore the influence of the synergistic effect of DLC1 and CDK6 on human breast cancer survival at the genetic, transcriptional, and translational levels. We found that high DLC1 and low CDK6 expression are associated with good prognosis. The DLC1 intronic SNP rs561681 is found to fit a recessive model, complying with the tumor suppressive role of DLC1. The heterozygote of the DLC1 SNP is found to increase the hazard when the CDK6 intronic SNP rs3731343 is rare homozygous, and it becomes protective when rs3731343 is common homozygous. We propose that DLC1 expression is the lowest in patients harboring the rare homozygote of rs561681 and functional DLC1 is the lowest when rs561681 is heterozygous and rs3731343 is rare homozygous. We are the first to report such synergistic effects of DLC1 and CDK6 on breast cancer survival at the transcriptional level, the overdominant model fitted by the SNP pair, and the dominant negative effect at the translational level. These findings link the germline genetic polymorphisms and synergistic effect of DLC1 and CDK6 with breast cancer progression, which provide the basis for experimentally elucidating the mechanisms driving differential tumor progression and avail in tailoring the clinical treatments for such patients based on their genetic susceptibility.
Keywords: CDK6; DLC1; breast cancer; cooperation; survival.
Copyright © 2015 Dai et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inactivation of the Dlc1 gene cooperates with downregulation of p15INK4b and p16Ink4a, leading to neoplastic transformation and poor prognosis in human cancer.Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 15;72(22):5900-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2368. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23010077 Free PMC article.
-
rs621554 single nucleotide polymorphism of DLC1 is associated with breast cancer susceptibility and prognosis.Mol Med Rep. 2016 May;13(5):4095-100. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4987. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26986853 Clinical Trial.
-
Dynein light chain 1 contributes to cell cycle progression by increasing cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity in estrogen-stimulated cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Jun 1;66(11):5941-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3480. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16740735
-
GAP-independent functions of DLC1 in metastasis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014 Mar;33(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s10555-013-9458-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014. PMID: 24338004 Review.
-
Tumor suppressor gene DLC1: Its modifications, interactive molecules, and potential prospects for clinical cancer application.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 1;182:264-275. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.022. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33836193 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) is a candidate diagnostic biomarker for early non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Jan;9(1):95-103. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.11.21. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117162 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Association of rs2237572 Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6 Gene with Breast Cancer in Iraq.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2021 Jul;36(3):304-311. doi: 10.1007/s12291-020-00895-5. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34220005 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between polymorphisms in the 3'untranslated region of the cyclin dependent kinase 6 gene and the human papillomavirus infection, and risk of cervical precancerous lesions.Biomed Rep. 2017 Jun;6(6):640-648. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.898. Epub 2017 May 3. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 28584635 Free PMC article.
-
CDK6 3'UTR polymorphisms alter the susceptibility to cervical cancer among Uyghur females.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 May;7(5):e626. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.626. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 30829464 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis identifies novel functional pathways of tumor suppressor DLC1 in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 2;13(10):e0204658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204658. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30278072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham R. S., Ballman K. V., Dispenzieri A., Grill D. E., Manske M. K., et al. , 2005. Functional gene expression analysis of clonal plasma cells identifies a unique molecular profile for light chain amyloidosis. Blood 105: 794–803. - PubMed
-
- Affymetrix, I., 2008 Affymetrix Genome-Wide Human SNP Nsp/Sty 6.0 User Guide in Data analysis.
-
- Blows F. M., Driver K. E., Schmidt M. K., Broeks A., Leeuwen F. E., et al. , 2010. Subtyping of breast cancer by immunohistochemistry to investigate a relationship between subtype and short and long term survival: A collaborative analysis of data for 10159 Cases from 12 Studies. PLoS Med. 7: e1000279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolstad B. M., Irizarry R. A., Astrand M., Speed T. P., 2003. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19: 185–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
