Hydroxyeyhyl starch: Controversies revisited
- PMID: 25425769
- PMCID: PMC4234780
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-9185.142801
Hydroxyeyhyl starch: Controversies revisited
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Hydroxyeyhyl starch: Controversies revisited.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul-Sep;34(3):427. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.243181. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30386044 Free PMC article.
Abstract
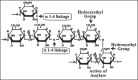
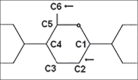
Hydroxyethyl starch (HES) family has been one of the cornerstones in fluid management for over four decades. Recent evidence from clinical studies and meta-analyses has raised few concerns about the safety of these fluids, especially in certain subpopulations of patients. High-quality clinical trials and meta-analyses have emphasized nephrotoxic effects, increased risk of bleeding, and a trend toward higher mortality in these patients after the use of HES solutions. Scientific evidence was derived from international guidelines, aggregated research literature, and opinion-based evidence was obtained from surveys and other activities (e.g., internet postings). On critical analysis of the current data available, it can be summarized that further large scale trials are still indicated before HES can be discarded.
Keywords: Controversies; colloids; hydroxyethyl starch.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Treib J, Baron JF, Grauer MT, Strauss RG. An international view of hydroxyethyl starches. Intensive Care Med. 1999;25:258–68. - PubMed
-
- Westphal M, James MF, Kozek-Langenecker S, Stocker R, Guidet B, Van Aken H. Hydroxyethyl starches: Different products — Different effects. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:187–202. - PubMed
-
- Ertmer C, Rehberg S, Van Aken H, Westphal M. Relevance of non-albumin colloids in intensive care medicine. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2009;23:193–212. - PubMed
-
- Van Der Linden P, James M, Mythen M, Weiskopf RB. Safety of modern starches used during surgery. Anesth Analg. 2013;116:35–48. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources