Optic nerve sheath diameter as a marker for evaluation and prognostication of intracranial pressure in Indian patients: An observational study
- PMID: 25425840
- PMCID: PMC4238090
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.144015
Optic nerve sheath diameter as a marker for evaluation and prognostication of intracranial pressure in Indian patients: An observational study
Abstract
Background and aims: The aim was to evaluate efficacy of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) by ultrasound as a noninvasive method for detecting raised intracranial pressure (ICP) in intensive care unit, to compare with computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings of raised ICP and to prognosticate ONSD value with treatment.
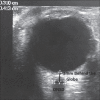
Materials and methods: We conducted a prospective, observational study on 101 adults by including 41 healthy individuals in group A as control and 60 patients in group B admitted with fever, headache, vomiting, and altered sensorium. We examined them in supine position using 10 MHz linear array probe on closed eyelid. ONSD was measured 3 mm behind the globe in each eye. A mean binocular ONSD > 4.6 mm in female and 4.8 mm in male was considered abnormal. Midline shift, edema, effacement or ONSD > 5.0 mm on T2 MRI suggestive of elevated ICP was used to evaluate ONSD accuracy.
Results: Group A mean ONSD was 4.6 mm in females and 4.8 mm in males. Group B mean ONSD for 17 females was 5.103 ± 0.6221 mm (P = 0.002) and for 43 males 5.081 ± 0.5799 mm (P = 0.032). Radiological sign of raised ICP was confirmed in 35 patients (females = 11 and males = 24) with high ONSD value. Sensitivity of detecting raised ICP by ONSD was 84.6% in females and 75% in males while specificity was 100% in both genders. Out of 25 patients without radiological signs of raised ICP 10 patients showed high ONSD (females = 4.735 mm and males = 4.907 mm). ONSD was well prognosticated with treatment modalities.
Conclusion: Bedside ocular ultrasonography for measuring ONSD can be used an early test for diagnosing raised ICP as it is a noninvasive, cost effective bedside test, which can be repeated for re-evaluation.
Keywords: Computed tomography; intensive care unit; magnetic resonance imaging; mannitol; optic nerve sheath diameter; raised intracranial pressure; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Utility of Bedside Ultrasound Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Screening Tool for raised Intracranial Pressure in Neurocritical Care Prospective Observational Study.J Assoc Physicians India. 2023 Jul;71(7):11-12. doi: 10.59556/japi.71.0287. J Assoc Physicians India. 2023. PMID: 37449686
-
Correlation of measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter using ultrasound with magnetic resonance imaging.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015 Aug;19(8):466-70. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.162465. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 26321806 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement: a means of detecting raised ICP in adult traumatic and non-traumatic neurosurgical patients.Am J Emerg Med. 2017 Jan;35(1):150-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.09.044. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 27852525
-
Optic nerve sheath diameters in nontraumatic brain injury: A scoping review and role in the intensive care unit.World J Crit Care Med. 2024 Sep 9;13(3):97205. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i3.97205. eCollection 2024 Sep 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39253313 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter by Bedside Ultrasound in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury Presenting to Emergency Department: A Review.Cureus. 2024 Jun 5;16(6):e61768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61768. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38975557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter and Its Postoperative Regression among Patients Undergoing Brain Tumor Resection in a Tertiary Care Center.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2022 Mar 10;13(2):270-275. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1744117. eCollection 2022 Apr. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2022. PMID: 35694055 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement using bedside ultrasound: Is it accurate?Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015 Aug;19(8):443-5. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.162456. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 26321801 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurements using ultrasonography to diagnose raised intracranial pressure in preeclampsia: an observational study.J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2023 Mar 15;24(1):5-11. doi: 10.4274/jtgga.galenos.2022.2022-3-3. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36919381 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter ultrasonography for elevated intracranial pressure detection.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020 May;7(5):865-868. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51054. Epub 2020 May 7. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32383326 Free PMC article.
-
Is Ocular Sonography a Reliable Method for the Assessment of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Children?J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021 Mar;10(1):14-22. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1716385. Epub 2020 Sep 7. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 33585057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vahedi K, Hofmeijer J, Juettler E, Vicaut E, George B, Algra A, et al. Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: A pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:215–22. - PubMed
-
- Ware AJ, D'Agostino AN, Combes B. Cerebral edema: A major complication of massive hepatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. 1971;61:877–84. - PubMed
-
- Quagliarello V, Scheld WM. Bacterial meningitis: Pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and progress. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:864–72. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen M, Brandt CT, Knudsen GM, Ostergaard C, Skinhøj P, Frimodt-Møller N, et al. Cerebral blood flow autoregulation in early experimental S. pneumoniae meningitis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2007;102:72–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
