Clinical features of organophosphate poisoning: A review of different classification systems and approaches
- PMID: 25425841
- PMCID: PMC4238091
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-5229.144017
Clinical features of organophosphate poisoning: A review of different classification systems and approaches
Abstract
Purpose: The typical toxidrome in organophosphate (OP) poisoning comprises of the Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Defecation, Gastric cramps, Emesis (SLUDGE) symptoms. However, several other manifestations are described. We review the spectrum of symptoms and signs in OP poisoning as well as the different approaches to clinical features in these patients.
Materials and methods: Articles were obtained by electronic search of PubMed(®) between 1966 and April 2014 using the search terms organophosphorus compounds or phosphoric acid esters AND poison or poisoning AND manifestations.
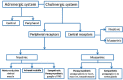
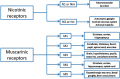
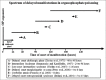
Results: Of the 5026 articles on OP poisoning, 2584 articles pertained to human poisoning; 452 articles focusing on clinical manifestations in human OP poisoning were retrieved for detailed evaluation. In addition to the traditional approach of symptoms and signs of OP poisoning as peripheral (muscarinic, nicotinic) and central nervous system receptor stimulation, symptoms were alternatively approached using a time-based classification. In this, symptom onset was categorized as acute (within 24-h), delayed (24-h to 2-week) or late (beyond 2-week). Although most symptoms occur with minutes or hours following acute exposure, delayed onset symptoms occurring after a period of minimal or mild symptoms, may impact treatment and timing of the discharge following acute exposure. Symptoms and signs were also viewed as an organ specific as cardiovascular, respiratory or neurological manifestations. An organ specific approach enables focused management of individual organ dysfunction that may vary with different OP compounds.
Conclusions: Different approaches to the symptoms and signs in OP poisoning may better our understanding of the underlying mechanism that in turn may assist with the management of acutely poisoned patients.
Keywords: Intermediate syndrome; manifestations; organophosphate; poisoning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Balme KH, Roberts JC, Glasstone M, Curling L, Rother HA, London L, et al. Pesticide poisonings at a tertiary children's hospital in South Africa: An increasing problem. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2010;48:928–34. - PubMed
-
- Peter JV, Jerobin J, Nair A, Bennett A, Samuel P, Chrispal A, et al. Clinical profile and outcome of patients hospitalized with dimethyl and diethyl organophosphate poisoning. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2010;48:916–23. - PubMed
-
- Peter JV, Cherian AM. Organic insecticides. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2000;28:11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
