Synthesis and κ-opioid receptor activity of furan-substituted salvinorin A analogues
- PMID: 25426797
- PMCID: PMC4281103
- DOI: 10.1021/jm501521d
Synthesis and κ-opioid receptor activity of furan-substituted salvinorin A analogues
Abstract
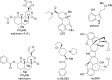
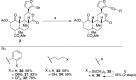
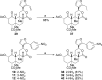
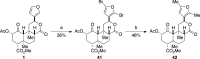
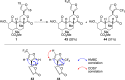
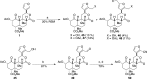
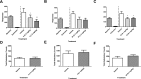
The neoclerodane diterpene salvinorin A, found in the leaves of Salvia divinorum, is a potent κ-opioid receptor agonist, making it an attractive scaffold for development into a treatment for substance abuse. Although several successful semisynthetic studies have been performed to elucidate structure-activity relationships, the lack of analogues with substitutions to the furan ring of salvinorin A has prevented a thorough understanding of its role in binding to the κ-opioid receptor. Herein we report the synthesis of several salvinorin A derivatives with modified furan rings. Evaluation of these compounds in a functional assay indicated that sterically less demanding substitutions are preferred, suggesting the furan ring is bound in a congested portion of the binding pocket. The most potent of the analogues successfully reduced drug-seeking behavior in an animal model of drug-relapse without producing the sedation observed with other κ-opioid agonists.
Figures

References
-
- Mansour A.; Fox C. A.; Burke S.; Meng F.; Thompson R. C.; Akil H.; Watson S. J. Mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: An in situ hybridization study. J. Compar. Neurol. 1994, 350, 412–438. - PubMed
-
- Mansour A.; Fox C. A.; Meng F.; Akil H.; Watson S. J. κ1 Receptor mRNA distribution in the rat CNS: Comparison to κ receptor binding and prodynorphin mRNA. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1994, 5, 124–144. - PubMed
-
- Minami M.; Satoh M. Molecular biology of the opioid receptors: Structures, functions and distributions. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 23, 121–145. - PubMed
-
- Preti A. New developments in the pharmacotherapy of cocaine abuse. Addict. Biol. 2007, 12, 133–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

