Initiation of electron transport chain activity in the embryonic heart coincides with the activation of mitochondrial complex 1 and the formation of supercomplexes
- PMID: 25427064
- PMCID: PMC4245138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113330
Initiation of electron transport chain activity in the embryonic heart coincides with the activation of mitochondrial complex 1 and the formation of supercomplexes
Abstract
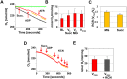
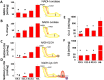
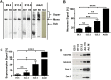
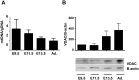
Mitochondria provide energy in form of ATP in eukaryotic cells. However, it is not known when, during embryonic cardiac development, mitochondria become able to fulfill this function. To assess this, we measured mitochondrial oxygen consumption and the activity of the complexes (Cx) 1 and 2 of the electron transport chain (ETC) and used immunoprecipitation to follow the generation of mitochondrial supercomplexes. We show that in the heart of mouse embryos at embryonic day (E) 9.5, mitochondrial ETC activity and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) are not coupled, even though the complexes are present. We show that Cx-1 of the ETC is able to accept electrons from the Krebs cycle, but enzyme assays that specifically measure electron flow to ubiquinone or Cx-3 show no activity at this early embryonic stage. At E11.5, mitochondria appear functionally more mature; ETC activity and OXPHOS are coupled and respond to ETC inhibitors. In addition, the assembly of highly efficient respiratory supercomplexes containing Cx-1, -3, and -4, ubiquinone, and cytochrome c begins at E11.5, the exact time when Cx-1 becomes functional activated. At E13.5, ETC activity and OXPHOS of embryonic heart mitochondria are indistinguishable from adult mitochondria. In summary, our data suggest that between E9.5 and E11.5 dramatic changes occur in the mitochondria of the embryonic heart, which result in an increase in OXPHOS due to the activation of complex 1 and the formation of supercomplexes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Ascuitto RJ, Ross-Ascuitto NT. Substrate metabolism in the developing heart. Semin Perinatol. 1996;20:542–563. - PubMed
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Jaswal JS. Energy metabolic phenotype of the cardiomyocyte during development, differentiation, and postnatal maturation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;56:130–140. - PubMed
-
- Baker CN, Ebert SN. Development of aerobic metabolism in utero: Requirement for mitochondrial function during embryonic and fetal periods. OA Biotechnology. 2013;2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

