Oxidative stress contributes to orthopedic trauma-induced acute kidney injury in obese rats
- PMID: 25428128
- PMCID: PMC4338927
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00537.2014
Oxidative stress contributes to orthopedic trauma-induced acute kidney injury in obese rats
Abstract
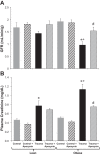
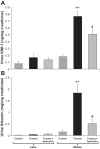
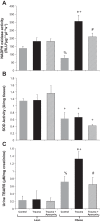
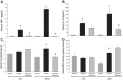
After trauma, obese patients have an increased risk of developing acute kidney injury (AKI). We have demonstrated that obese Zucker (OZ) rats, but not lean Zucker (LZ) rats, develop AKI 24 h after orthopedic trauma. ROS have been implicated in the pathophysiology of AKI in models of critical illness. However, the contribution of ROS to trauma-induced AKI in the setting of obesity has not been determined. We hypothesized that AKI in OZ rats after trauma is mediated by increased oxidative stress. Male LZ and OZ rats were divided into control and trauma groups, with a subset receiving treatment after trauma with the antioxidant apocynin (50 mg/kg ip, 2 mM in drinking water). The day after trauma, glomerular filtration rate, plasma creatinine, urine kidney injury molecule-1, and albumin excretion as well as renal oxidant and antioxidant activity were measured. After trauma, compared with LZ rats, OZ rats exhibited a significant decrease in glomerular filtration rate along with significant increases in plasma creatinine and urine kidney injury molecule-1 and albumin excretion. Additionally, oxidative stress was significantly increased in OZ rats, as evidenced by increased renal NADPH oxidase activity and urine lipid peroxidation products (thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances), and OZ rats also had suppressed renal superoxide dismutase activity. Apocynin treatment significantly decreased oxidative stress and AKI in OZ rats but had minimal effects in LZ rats. These results suggest that ROS play an important role in AKI in OZ rats after traumatic injury and that ROS may be a potential future therapeutic target in the obese after trauma.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; inflammation; obesity; reactive oxygen species; trauma.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Abilés J, de la Cruz AP, Castaño J, Rodríguez-Elvira M, Aguayo E, Moreno-Torres R, Llopis J, Aranda P, Argüelles S, Ayala A, de la Quintana AM, Planells EM. Oxidative stress is increased in critically ill patients according to antioxidant vitamins intake, independent of severity: a cohort study. Crit Care 10: R146, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87: 245–313, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 380: 756–766, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Belmont PJ Jr, Garcia EJ, Romano D, Bader JO, Nelson KJ, Schoenfeld AJ. Risk factors for complications and in-hospital mortality following hip fractures: a study using the National Trauma Data Bank. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134: 597–604, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

