An evaluation of volume-based morphometry for prediction of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 25429357
- PMCID: PMC4238047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.11.001
An evaluation of volume-based morphometry for prediction of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
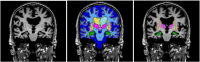
Voxel-based morphometry from conventional T1-weighted images has proved effective to quantify Alzheimer's disease (AD) related brain atrophy and to enable fairly accurate automated classification of AD patients, mild cognitive impaired patients (MCI) and elderly controls. Little is known, however, about the classification power of volume-based morphometry, where features of interest consist of a few brain structure volumes (e.g. hippocampi, lobes, ventricles) as opposed to hundreds of thousands of voxel-wise gray matter concentrations. In this work, we experimentally evaluate two distinct volume-based morphometry algorithms (FreeSurfer and an in-house algorithm called MorphoBox) for automatic disease classification on a standardized data set from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Results indicate that both algorithms achieve classification accuracy comparable to the conventional whole-brain voxel-based morphometry pipeline using SPM for AD vs elderly controls and MCI vs controls, and higher accuracy for classification of AD vs MCI and early vs late AD converters, thereby demonstrating the potential of volume-based morphometry to assist diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Brain morphometry; Classification; Image segmentation; Magnetic resonance imaging; Mild cognitive impairment; Support vector machine.
Figures


References
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage. 2007;38(1):95–113. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J. Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging; London, UK: 2010. VBM tutorial. (Tech. rep).
-
- Ashburner J., Friston K. Voxel-based morphometry — the methods. NeuroImage. 2000;11(6):805–821. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J., Friston K. Unified segmentation. NeuroImage. 2005;26(3):839–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

