Non-coding RNA regulation in pathogenic bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 25429360
- PMCID: PMC4228915
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00162
Non-coding RNA regulation in pathogenic bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells
Abstract
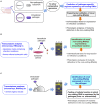
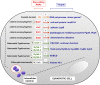
Intracellular bacterial pathogens have evolved distinct lifestyles inside eukaryotic cells. Some pathogens coexist with the infected cell in an obligate intracellular state, whereas others transit between the extracellular and intracellular environment. Adaptation to these intracellular lifestyles is regulated in both space and time. Non-coding small RNAs (sRNAs) are post-transcriptional regulatory molecules that fine-tune important processes in bacterial physiology including cell envelope architecture, intermediate metabolism, bacterial communication, biofilm formation, and virulence. Recent studies have shown production of defined sRNA species by intracellular bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells. The molecules targeted by these sRNAs and their expression dynamics along the intracellular infection cycle remain, however, poorly characterized. Technical difficulties linked to the isolation of "intact" intracellular bacteria from infected host cells might explain why sRNA regulation in these specialized pathogens is still a largely unexplored field. Transition from the extracellular to the intracellular lifestyle provides an ideal scenario in which regulatory sRNAs are intended to participate; so much work must be done in this direction. This review focuses on sRNAs expressed by intracellular bacterial pathogens during the infection of eukaryotic cells, strategies used with these pathogens to identify sRNAs required for virulence, and the experimental technical challenges associated to this type of studies. We also discuss varied techniques for their potential application to study RNA regulation in intracellular bacterial infections.
Keywords: bacteria; intracellular infection; non-coding RNA; pathogen; regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of Salmonella small RNA expression in non-growing bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells.RNA Biol. 2012 Apr;9(4):469-88. doi: 10.4161/rna.19317. Epub 2012 Feb 16. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22336761
-
A novel antisense RNA from the Salmonella virulence plasmid pSLT expressed by non-growing bacteria inside eukaryotic cells.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 31;8(10):e77939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077939. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205037 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs, 5' UTR elements and RNA-binding proteins in intracellular bacteria: impact on metabolism and virulence.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015 May;39(3):331-49. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv022. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26009640 Review.
-
Bacterial sRNAs: regulation in stress.Int J Med Microbiol. 2013 Jul;303(5):217-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23660175 Review.
-
Small RNA-mediated regulation in bacteria: A growing palette of diverse mechanisms.Gene. 2018 May 20;656:60-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.068. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29501814 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlamydia trachomatis In Vivo to In Vitro Transition Reveals Mechanisms of Phase Variation and Down-Regulation of Virulence Factors.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133420. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26207372 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Ribonucleases and sRNAs in the Virulence of Foodborne Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2017 May 19;8:910. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00910. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28579982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin accessibility dynamics of Chlamydia-infected epithelial cells.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2020 Oct 27;13(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13072-020-00368-2. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2020. PMID: 33109274 Free PMC article.
-
What Is in a Cat Scratch? Growth of Bartonella henselae in a Biofilm.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 14;9(4):835. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040835. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33919891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Small RNA RyhB Homologs from Salmonella Typhimurium Restrain the Intracellular Growth and Modulate the SPI-1 Gene Expression within RAW264.7 Macrophages.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 18;9(3):635. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030635. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33803635 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

