The h-index in medical education: an analysis of medical education journal editorial boards
- PMID: 25429724
- PMCID: PMC4251938
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-014-0251-8
The h-index in medical education: an analysis of medical education journal editorial boards
Abstract
Background: Disciplines differ in their authorship and citation practices, thus discipline-specific h-index norms are desirable. Thus the goal of this study was to examine the relationship between the h-index and academic rank in the field of medical education, and the differences in the h-index between MD's and PhD's in this field.
Methods: Due to the absence of a formalized registry of medical educators, we sampled available editorial board membership (considered a proxy for identifying 'career' medical educators) to establish h-index values. These were determined using Web of Science (WoS) and Google Scholar (GS), and internet searching was used to determine their academic rank. The correlation between authors' h-indices derived from WoS and GS was also determined.
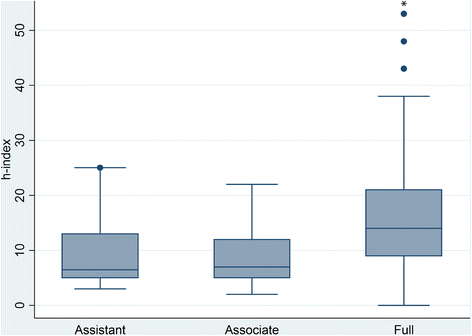
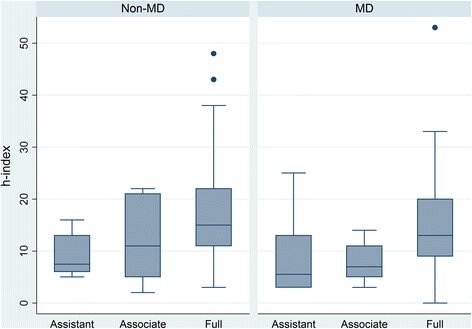
Results: 130 editors were identified (95 full professors, 21 associate professors, 14 assistant professors). A significant difference was noted between the h-indices of full professors and associate/assistant professors (p < .001). Median h-indices equaled 14 for full professors (Interquartile range [IQR] =11); 7 for associate professors (IQR =7) and 6.5 for assistant professors (IQR = 8). h-indices of MD's and PhD's did not differ significantly. Moderate correlation between GS and WOS h-indices was noted R = 0.46, p < .001.
Conclusions: The results provide some guidance as to the expected h-indices of a select group of medical educators. No differences appear to exist between assistant professor and associate professor ranks or between MD's and PhD's.
Figures
References
-
- Bordons M, Fernandez MT, Gomez I. Advantages and limitations of the use of impact factor measures for the assessment of research performance. Scientometrics. 2002;53:195–206. doi: 10.1023/A:1014800407876. - DOI
-
- Bornmann L, Daniel HD. What do we know about the h index? J Am Soc Inform Sci. 2007;58:1381–1385. doi: 10.1002/asi.20609. - DOI
-
- Rousseau R. Reflections on recent developments of the h-index and h-type indices. In: Kretschmer H, Havemann F, editors. Proceedings of WIS 2008, Fourth International Conference on Webometrics, Informetrics and Scientometrics & Ninth COLLNET Meeting. Berlin: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Institute for Library and Information Science (IBI); 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

