Efficacy of behavioural interventions for transport behaviour change: systematic review, meta-analysis and intervention coding
- PMID: 25429846
- PMCID: PMC4267710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-014-0133-9
Efficacy of behavioural interventions for transport behaviour change: systematic review, meta-analysis and intervention coding
Abstract
Background: Reducing reliance on motorised transport and increasing use of more physically active modes of travel may offer an opportunity to address physical inactivity. This review evaluates the evidence for the effects of behavioural interventions to reduce car use for journeys made by adults and codes intervention development and content.
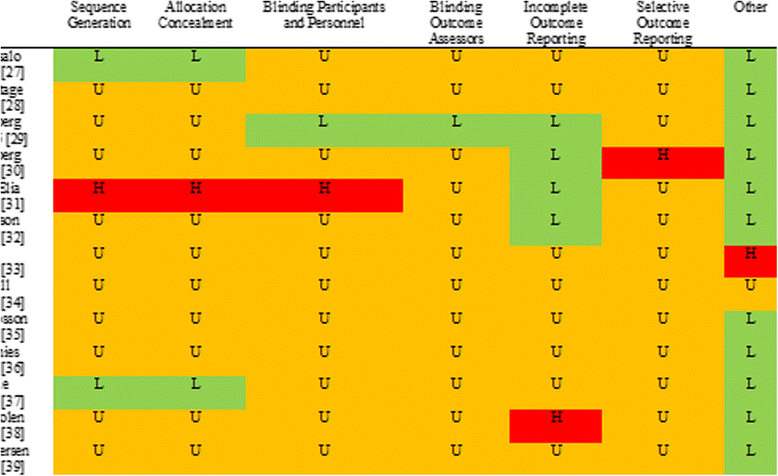
Methods: The review follows the procedure stated in the registration protocol published in the PROSPERO database (registration number CRD42011001797). Controlled studies evaluating behavioural interventions to reduce car use compared with no interventions or alternative interventions on outcome measures of transport behaviours taken in adult participants are included in this review. Searches were conducted on all records in Applied Social Sciences Index and Abstracts (ASSIA), Ovid Embase, Ovid Medline, Ovid PsycInfo, Scopus, Sociological Abstracts, Transportation Research Information Service (TRIS), Transportation Research International Documentation (TRID), and Web of Science databases. Peer reviewed publications in English language meeting the inclusion criteria are eligible. Methodological quality is assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool. Interventions are categorised in terms of behavioural frameworks, theories and techniques.
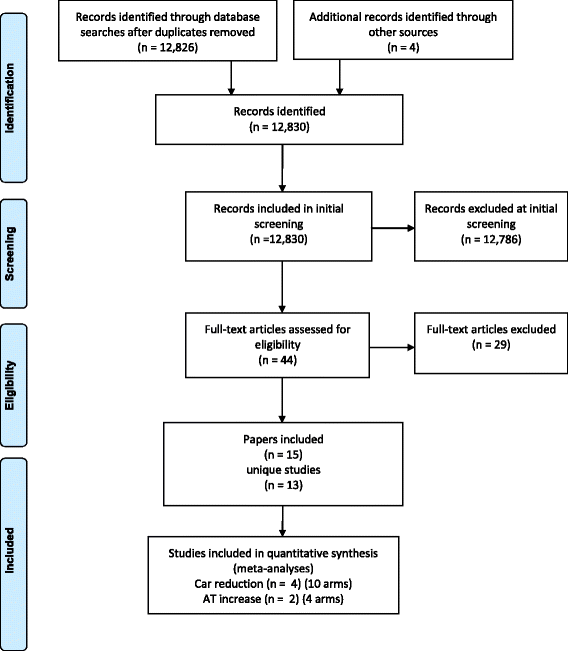
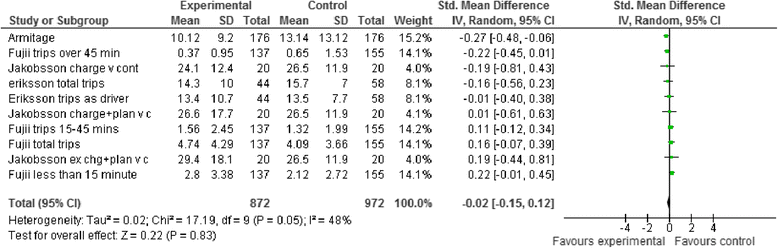
Results: 15 full text articles are included, representing 13 unique studies, with 4895 participants and 27 intervention arms. Risk of bias across the review is appraised as considerable due to the unclear methodological quality of individual studies. Heterogeneity of included studies is considerable. Meta-analyses reveal no significant effect on reduction of frequency of car use or on increasing the proportion of journeys by alternative, more active modes of transport. There is insufficient data relating to alternative outcomes such as distance and duration which may have important health implications. Interventions were top-down but could not be described as theory-based. Intervention efficacy was associated with the use of a combination of information provision and behavioural regulation techniques. There was a lack of consideration of opportunity for change and behaviour in context.
Conclusions: There is no evidence for the efficacy of existing behavioural interventions to reduce car trips included in this review. The evidence for efficacy of behavioural interventions to decrease distance and duration of car journeys is limited and inconclusive. Overall the evidence is highly heterogeneous and is at considerable risk of bias. Future research should investigate alternative behavioural interventions in high quality, controlled studies informed by existing evidence, theory, and viewers of potential users. Future intervention studies should increase scientific rigour, include objective outcome measures, and incorporate thorough evaluations as standard.
Figures
References
-
- NICE guidance: Walking and Cycling : Local Measures to Promote Walking and Cycling as Forms of Travel or Recreation. 2012 (November)
-
- The All Party Parliamentary Cycling Group: Get Britain Cycling 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources