Phospholipid-binding sites of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN): exploring the mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate activation
- PMID: 25429968
- PMCID: PMC4340405
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.588590
Phospholipid-binding sites of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN): exploring the mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate activation
Abstract
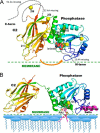
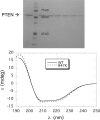
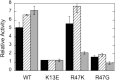
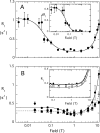
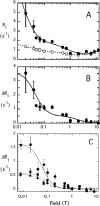
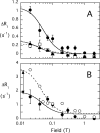
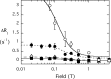
The lipid phosphatase activity of the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is enhanced by the presence of its biological product, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2). This enhancement is suggested to occur via the product binding to the N-terminal region of the protein. PTEN effects on short-chain phosphoinositide (31)P linewidths and on the full field dependence of the spin-lattice relaxation rate (measured by high resolution field cycling (31)P NMR using spin-labeled protein) are combined with enzyme kinetics with the same short-chain phospholipids to characterize where PI(4,5)P2 binds on the protein. The results are used to model a discrete site for a PI(4,5)P2 molecule close to, but distinct from, the active site of PTEN. This PI(4,5)P2 site uses Arg-47 and Lys-13 as phosphate ligands, explaining why PTEN R47G and K13E can no longer be activated by that phosphoinositide. Placing a PI(4,5)P2 near the substrate site allows for proper orientation of the enzyme on interfaces and should facilitate processive catalysis.
Keywords: 31P Field Cycling; Enzyme Kinetics; Micelles; Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR); Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN); Phosphatidylinositol Phosphatase; Phosphoinositide; Phospholipid-binding Site; Spin-labeled Protein.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Song M. S., Salmena L., Pandolfi P. P. (2012) The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 283–296 - PubMed
-
- Salmena L., Carracedo A., Pandolfi P. P. (2008) Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell 133, 403–414 - PubMed
-
- Chang N., El-Hayek Y. H., Gomez E., Wan Q. (2007) Phosphatase PTEN in neuronal injury and brain disorders. Trends Neurosci. 30, 581–586 - PubMed
-
- Maehama T., Dixon J. E. (1998) The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 13375–13378 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

