SNP-Seek database of SNPs derived from 3000 rice genomes
- PMID: 25429973
- PMCID: PMC4383887
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1039
SNP-Seek database of SNPs derived from 3000 rice genomes
Abstract
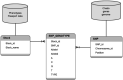
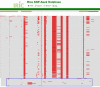
We have identified about 20 million rice SNPs by aligning reads from the 3000 rice genomes project with the Nipponbare genome. The SNPs and allele information are organized into a SNP-Seek system (http://www.oryzasnp.org/iric-portal/), which consists of Oracle database having a total number of rows with SNP genotypes close to 60 billion (20 M SNPs × 3 K rice lines) and web interface for convenient querying. The database allows quick retrieving of SNP alleles for all varieties in a given genome region, finding different alleles from predefined varieties and querying basic passport and morphological phenotypic information about sequenced rice lines. SNPs can be visualized together with the gene structures in JBrowse genome browser. Evolutionary relationships between rice varieties can be explored using phylogenetic trees or multidimensional scaling plots.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Tai A.P.K., Martin M.V., Heald C.L. Threat to future global food security from climate change and ozone air pollution. Nat. Clim. Change. 2014;4:817–821.
-
- Fahad S., Nie L., Khan F.A., Chen Y., Hussain S., Wu C., Xiong D., Jing W., Saud S., Khan F.A., et al. Disease resistance in rice and the role of molecular breeding in protecting rice crops against diseases. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014;36:1407–1420. - PubMed
-
- Hu H., Xiong L. Genetic engineering and breeding of drought-resistant crops. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014;65:715–741. - PubMed
-
- Gao Z.Y., Zhao S.C., He W.M., Guo L.B., Peng Y.L., Wang J.J., Guo X.S., Zhang X.M., Rao Y.C., Zhang C., et al. Dissecting yield-associated loci in super hybrid rice by resequencing recombinant inbred lines and improving parental genome sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013;110:14492–14497. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

