Simplified post processing of cine DENSE cardiovascular magnetic resonance for quantification of cardiac mechanics
- PMID: 25430079
- PMCID: PMC4246464
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-014-0094-9
Simplified post processing of cine DENSE cardiovascular magnetic resonance for quantification of cardiac mechanics
Abstract
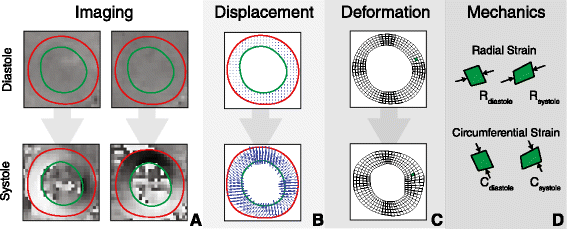
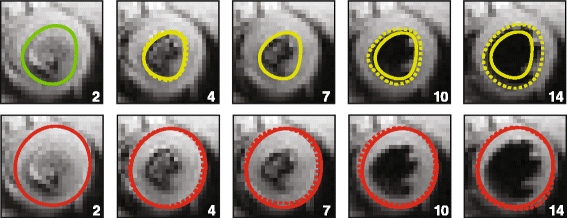
Background: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance using displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) is capable of assessing advanced measures of cardiac mechanics such as strain and torsion. A potential hurdle to widespread clinical adoption of DENSE is the time required to manually segment the myocardium during post-processing of the images. To overcome this hurdle, we proposed a radical approach in which only three contours per image slice are required for post-processing (instead of the typical 30-40 contours per image slice). We hypothesized that peak left ventricular circumferential, longitudinal and radial strains and torsion could be accurately quantified using this simplified analysis.
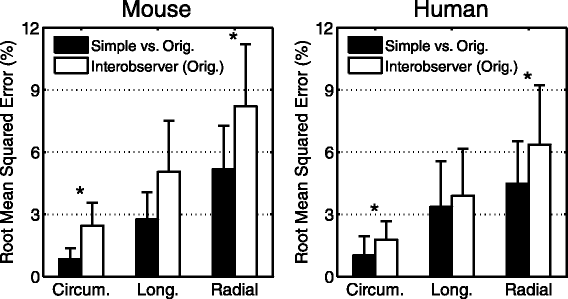
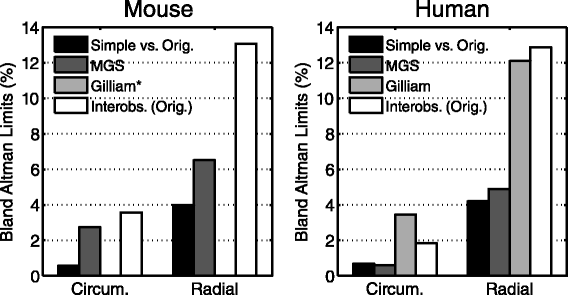
Methods and results: We tested our hypothesis on a large multi-institutional dataset consisting of 541 DENSE image slices from 135 mice and 234 DENSE image slices from 62 humans. We compared measures of cardiac mechanics derived from the simplified post-processing to those derived from original post-processing utilizing the full set of 30-40 manually-defined contours per image slice. Accuracy was assessed with Bland-Altman limits of agreement and summarized with a modified coefficient of variation. The simplified technique showed high accuracy with all coefficients of variation less than 10% in humans and 6% in mice. The accuracy of the simplified technique was also superior to two previously published semi-automated analysis techniques for DENSE post-processing.
Conclusions: Accurate measures of cardiac mechanics can be derived from DENSE cardiac magnetic resonance in both humans and mice using a simplified technique to reduce post-processing time by approximately 94%. These findings demonstrate that quantifying cardiac mechanics from DENSE data is simple enough to be integrated into the clinical workflow.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of left ventricular strains and torsion derived from feature tracking and DENSE CMR.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018 Sep 13;20(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12968-018-0485-4. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018. PMID: 30208894 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of cine displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) cardiovascular magnetic resonance for measuring left ventricular strains, torsion, and synchrony in mice.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013 Aug 27;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-15-71. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013. PMID: 23981339 Free PMC article.
-
2D cine DENSE with low encoding frequencies accurately quantifies cardiac mechanics with improved image characteristics.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015 Nov 4;17:93. doi: 10.1186/s12968-015-0196-z. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015. PMID: 26538111 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial tagging by cardiovascular magnetic resonance: evolution of techniques--pulse sequences, analysis algorithms, and applications.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011 Jul 28;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-13-36. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011. PMID: 21798021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated motion estimation for 2-D cine DENSE MRI.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012 Sep;31(9):1669-81. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2012.2195194. Epub 2012 May 3. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22575669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring Cardiac Dyssynchrony with DENSE (Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echoes)-A Systematic Review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 18;24(9):261. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2409261. eCollection 2023 Sep. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076380 Free PMC article.
-
Improved computation of Lagrangian tissue displacement and strain for cine DENSE MRI using a regularized spatiotemporal least squares method.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 16;10:1095159. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1095159. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37008315 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2014.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015 Nov 20;17:99. doi: 10.1186/s12968-015-0203-4. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2015. PMID: 26589839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An interactive videogame designed to improve respiratory navigator efficiency in children undergoing cardiovascular magnetic resonance.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2016 Sep 6;18(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12968-016-0272-z. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2016. PMID: 27599620 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fully-automated global and segmental strain analysis of DENSE cardiovascular magnetic resonance using deep learning for segmentation and phase unwrapping.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 Mar 11;23(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00712-9. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33691739 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

