Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target
- PMID: 25430794
- PMCID: PMC4246208
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07245
Non-antibiotic quorum sensing inhibitors acting against N-acyl homoserine lactone synthase as druggable target
Abstract
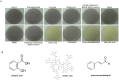
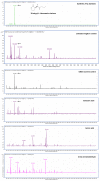
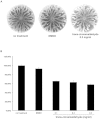
N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHL)-based quorum sensing (QS) is important for the regulation of proteobacterial virulence determinants. Thus, the inhibition of AHL synthases offers non-antibiotics-based therapeutic potentials against QS-mediated bacterial infections. In this work, functional AHL synthases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasI and RhlI were heterologously expressed in an AHL-negative Escherichia coli followed by assessments on their AHLs production using AHL biosensors and high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LCMS). These AHL-producing E. coli served as tools for screening AHL synthase inhibitors. Based on a campaign of screening synthetic molecules and natural products using our approach, three strongest inhibitors namely are salicylic acid, tannic acid and trans-cinnamaldehyde have been identified. LCMS analysis further confirmed tannic acid and trans-cinnemaldehyde efficiently inhibited AHL production by RhlI. We further demonstrated the application of trans-cinnemaldehyde inhibiting Rhl QS system regulated pyocyanin production in P. aeruginosa up to 42.06%. Molecular docking analysis suggested that trans-cinnemaldehyde binds to the LasI and EsaI with known structures mainly interacting with their substrate binding sites. Our data suggested a new class of QS-inhibiting agents from natural products targeting AHL synthase and provided a potential approach for facilitating the discovery of anti-QS signal synthesis as basis of novel anti-infective approach.
Figures


References
-
- Cámara M., Williams P. & Hardman A. Controlling infection by tuning in and turning down the volume of bacterial small-talk. Lancet Infect Dis 2, 667–676 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Fuqua C. & Greenberg E. P. Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 685–695 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Williams P. & Cámara M. Quorum sensing and environmental adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a tale of regulatory networks and multifunctional signal molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12, 182–191 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Antunes L. C. M., Ferreira R. B. R., Buckner M. M. C. & Finlay B. B. Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology 156, 2271–2282 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

