Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 25430866
- PMCID: PMC4751590
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd4477
Managing diabetes with nanomedicine: challenges and opportunities
Abstract
Nanotechnology-based approaches hold substantial potential for improving the care of patients with diabetes. Nanoparticles are being developed as imaging contrast agents to assist in the early diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Glucose nanosensors are being incorporated in implantable devices that enable more accurate and patient-friendly real-time tracking of blood glucose levels, and are also providing the basis for glucose-responsive nanoparticles that better mimic the body's physiological needs for insulin. Finally, nanotechnology is being used in non-invasive approaches to insulin delivery and to engineer more effective vaccine, cell and gene therapies for type 1 diabetes. Here, we analyse the current state of these approaches and discuss key issues for their translation to clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing interests: see Web version for details.
Figures


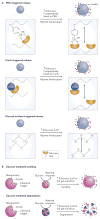
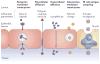
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — 2014. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:S14–S80. - PubMed
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, et al. Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D. The accelerating epidemic of childhood diabetes. Lancet. 2009;373:1999–2000. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman SM, DiLorenzo TP. A comprehensive guide to antibody and T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:359–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

