A common variant in RAB27A gene is associated with fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels in adults
- PMID: 25431337
- PMCID: PMC4405185
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12461
A common variant in RAB27A gene is associated with fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels in adults
Abstract
Background: Exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) is a biomarker for eosinophilic inflammation in the airways and for responsiveness to corticosteroids in asthmatics.
Objective: We sought to identify in adults the genetic determinants of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) levels and to assess whether environmental and disease-related factors influence these associations.
Methods: We performed a genome-wide association study of FeNO through meta-analysis of two independent discovery samples of European ancestry: the outbred EGEA study (French Epidemiological study on the Genetics and Environment of Asthma, N = 610 adults) and the Hutterites (N = 601 adults), a founder population living on communal farms. Replication of main findings was assessed in adults from an isolated village in Sardinia (Talana study, N = 450). We then investigated the influence of asthma, atopy and tobacco smoke exposure on these genetic associations, and whether they were also associated with FeNO values in children of the EAGLE (EArly Genetics & Lifecourse Epidemiology, N = 8858) consortium.
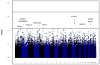
Results: We detected a common variant in RAB27A (rs2444043) associated with FeNO that reached the genome-wide significant level (P = 1.6 × 10(-7) ) in the combined discovery and replication adult data sets. This SNP belongs to member of RAS oncogene family (RAB27A) and was associated with an expression quantitative trait locus for RAB27A in lymphoblastoid cell lines from asthmatics. A second suggestive locus (rs2194437, P = 8.9 × 10(-7) ) located nearby the sodium/calcium exchanger 1 (SLC8A1) was mainly detected in atopic subjects and influenced by inhaled corticosteroid use. These two loci were not associated with childhood FeNO values.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: This study identified a common variant located in RAB27A gene influencing FeNO levels specifically in adults and with a biological relevance to the regulation of FeNO levels. This study provides new insight into the biological mechanisms underlying FeNO levels in adults.
Keywords: airway inflammation; asthma; atopy; exhaled nitric oxide; genetics; genome-wide association study.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Liesbeth Duijts is the recipient of a European Respiratory Society/Marie Curie Joint Research Fellowship and from the Lung Foundation Netherlands (no 3.2.12.089; 2012). The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ricciardolo FL, Di Stefano A, Sabatini F, Folkerts G. Reactive nitrogen species in the respiratory tract. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;533:240–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

