A plant-based diet, atherogenesis, and coronary artery disease prevention
- PMID: 25431999
- PMCID: PMC4315380
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/14-036
A plant-based diet, atherogenesis, and coronary artery disease prevention
Abstract
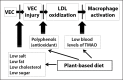
A plant-based diet is increasingly becoming recognized as a healthier alternative to a diet laden with meat. Atherosclerosis associated with high dietary intake of meat, fat, and carbohydrates remains the leading cause of mortality in the US. This condition results from progressive damage to the endothelial cells lining the vascular system, including the heart, leading to endothelial dysfunction. In addition to genetic factors associated with endothelial dysfunction, many dietary and other lifestyle factors, such as tobacco use, high meat and fat intake, and oxidative stress, are implicated in atherogenesis. Polyphenols derived from dietary plant intake have protective effects on vascular endothelial cells, possibly as antioxidants that prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein. Recently, metabolites of L-carnitine, such as trimethylamine-N-oxide, that result from ingestion of red meat have been identified as a potential predictive marker of coronary artery disease (CAD). Metabolism of L-carnitine by the intestinal microbiome is associated with atherosclerosis in omnivores but not in vegetarians, supporting CAD benefits of a plant-based diet. Trimethylamine-N-oxide may cause atherosclerosis via macrophage activation. We suggest that a shift toward a plant-based diet may confer protective effects against atherosclerotic CAD by increasing endothelial protective factors in the circulation while reducing factors that are injurious to endothelial cells. The relative ratio of protective factors to injurious endothelial exposure may be a novel approach to assessing an objective dietary benefit from a plant-based diet. This review provides a mechanistic perspective of the evidence for protection by a plant-based diet against atherosclerotic CAD.
Figures
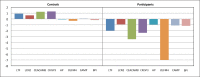
Gene Symbol = Gene Name (Gene Ontology Biologic Process)
LTF = lactotransferrin (immune response)
LCN2 = lipocalin (transporter activity)
CEACAM8 = carcinoembryonic antigen-related (immune response)
CRISP3 = cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 (immune response; defense response)
HP = haptoglobin protein (defense response)
OLFM4 = olfactomedin4 (cell adhesion)
CAMP = cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (defense response)
BPI = bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (immune response; lipid binding)
References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014 Jan 21;129(3):e28–e292. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000441139.02102.80. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999 Jan 14;340(2):115–26. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199901143400207. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BJ, Bartolotto C. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013 Spring;17(2):61–6. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7812/TPP/12-085. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blaney D, Diehl H. The optimal diet: the official CHIP cookbook. Hagerstown, MD: Autumn House Publishing; 2009. Jan 1,
-
- Berkow SE, Barnard N. Vegetarian diets and weight status. Nutr Rev. 2006 Apr;64(4):175–88. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00200.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

