Stromal androgen receptor roles in the development of normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia, and prostate cancer
- PMID: 25432062
- PMCID: PMC4305176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.10.012
Stromal androgen receptor roles in the development of normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia, and prostate cancer
Abstract
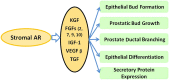
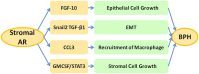
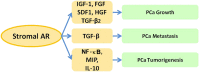
The prostate is an androgen-sensitive organ that needs proper androgen/androgen receptor (AR) signals for normal development. The progression of prostate diseases, including benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa), also needs proper androgen/AR signals. Tissue recombination studies report that stromal, but not epithelial, AR plays more critical roles via the mesenchymal-epithelial interactions to influence the early process of prostate development. However, in BPH and PCa, much more attention has been focused on epithelial AR roles. However, accumulating evidence indicates that stromal AR is also irreplaceable and plays critical roles in prostate disease progression. Herein, we summarize the roles of stromal AR in the development of normal prostate, BPH, and PCa, with evidence from the recent results of in vitro cell line studies, tissue recombination experiments, and AR knockout animal models. Current evidence suggests that stromal AR may play positive roles to promote BPH and PCa progression, and targeting stromal AR selectively with AR degradation enhancer, ASC-J9, may allow development of better therapies with fewer adverse effects to battle BPH and PCa.
Copyright © 2015 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hayward S.W., Baskin L.S., Haughney P.C., Foster B.A., Cunha A.R., Dahiya R., Prins G.S., Cunha G.R. Stromal development in the ventral prostate, anterior prostate and seminal vesicle of the rat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1996;155:94–103. - PubMed
-
- Heinlein C.A., Chang C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:276–308. - PubMed
-
- Huggins C., Hodges C.V. Studies on prostatic cancer, I: the effect of castration, of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. CA Cancer J Clin. 1972;22:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Shimazaki J., Kurihara H., Ito Y., Shida K. Testosterone metabolism in prostate: formation of androstan-17-beta-ol-3-one and androst-4-ene-3, 17-dione, and inhibitory effect of natural and synthetic estrogens. Gunma J Med Sci. 1965;14:313–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

