Tumor-induced myeloid dysfunction and its implications for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 25432147
- PMCID: PMC4282948
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-014-1639-3
Tumor-induced myeloid dysfunction and its implications for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
Immune function relies on an appropriate balance of the lymphoid and myeloid responses. In the case of neoplasia, this balance is readily perturbed by the dramatic expansion of immature or dysfunctional myeloid cells accompanied by a reciprocal decline in the quantity/quality of the lymphoid response. In this review, we seek to: (1) define the nature of the atypical myelopoiesis observed in cancer patients and the impact of this perturbation on clinical outcomes; (2) examine the potential mechanisms underlying these clinical manifestations; and (3) explore potential strategies to restore normal myeloid cell differentiation to improve activation of the host antitumor immune response. We posit that fundamental alterations in myeloid homeostasis triggered by the neoplastic process represent critical checkpoints that govern therapeutic efficacy, as well as offer novel cellular-based biomarkers for tracking changes in disease status or relapse.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
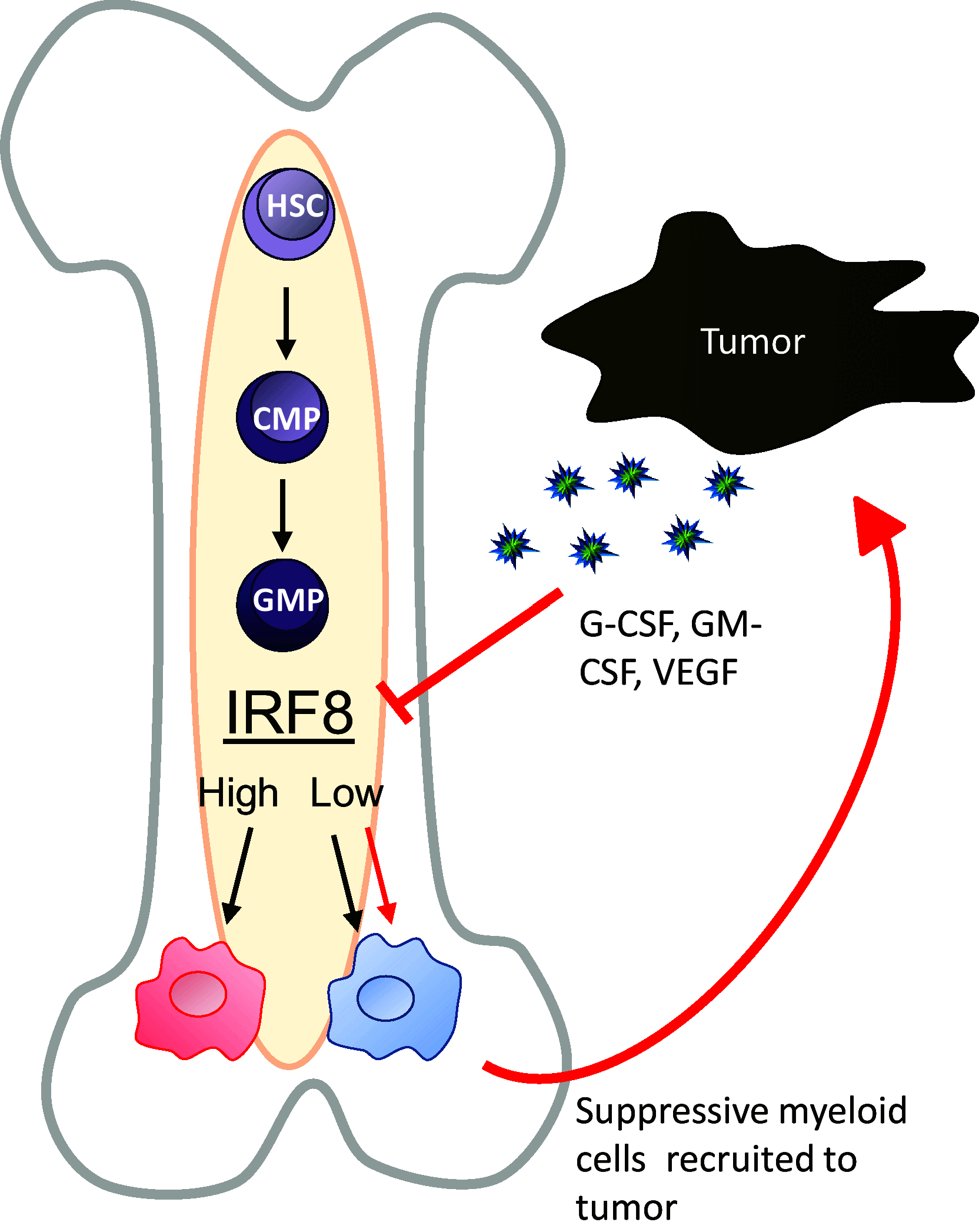
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Gabrilovich D. Mechanisms and functional significance of tumour-induced dendritic-cell defects. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(12):941–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

