Afatinib versus placebo as adjuvant therapy after chemoradiation in a double-blind, phase III study (LUX-Head & Neck 2) in patients with primary unresected, clinically intermediate-to-high-risk head and neck cancer: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25432788
- PMCID: PMC4289298
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-469
Afatinib versus placebo as adjuvant therapy after chemoradiation in a double-blind, phase III study (LUX-Head & Neck 2) in patients with primary unresected, clinically intermediate-to-high-risk head and neck cancer: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Over 50% of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) present with locoregionally advanced disease. Those at intermediate-to-high risk of recurrence after definitive therapy exhibit advanced disease based on tumour size or lymph node involvement, non-oropharynx primary sites, human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative oropharyngeal cancer, or HPV-positive oropharynx cancer with smoking history (>10-pack-years). Non-surgical approaches include concurrent chemoradiotherapy, induction chemotherapy followed by definitive radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy, or radiotherapy alone. Following locoregional therapies (including surgical salvage of residual cervical nodes), no standard intervention exists. Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), an ErbB family member, is associated with poor prognosis in HNSCC. EGFR-targeted cetuximab is the only targeted therapy that impacts overall survival and is approved for HNSCC in the USA or Europe. However, resistance often occurs, and new approaches, such as targeting multiple ErbB family members, may be required. Afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, demonstrated antiproliferative activity in preclinical models and comparable clinical efficacy with cetuximab in a randomized phase II trial in recurrent or metastatic HNSCC. LUX-Head & Neck 2, a phase III study, will assess adjuvant afatinib versus placebo following chemoradiotherapy in primary unresected locoregionally advanced intermediate-to-high-risk HNSCC.
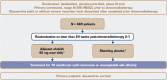
Methods/design: Patients with primary unresected locoregionally advanced HNSCC, in good clinical condition with unfavourable risk of recurrence, and no evidence of disease after chemoradiotherapy will be randomized 2:1 to oral once-daily afatinib (40 mg starting dose) or placebo. As HPV status will not be determined for eligibility, unfavourable risk is defined as non-oropharynx primary site or oropharynx cancer in patients with a smoking history (>10 pack-years). Treatment will continue for 18 months or until recurrence or unacceptable adverse events occur. The primary endpoint measure is duration of disease-free survival; secondary endpoint measures are disease-free survival rate at 2 years, overall survival, health-related quality of life and safety.
Discussion: Given the unmet need in the adjuvant treatment of intermediate-to-high-risk HNSCC patients, it is expected that LUX-Head & Neck 2 will provide new insights into treatment in this setting and might demonstrate the ability of afatinib to significantly improve disease-free survival, compared with placebo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01345669.
Figures
References
-
- GLOBOCAN: Estimated Cancer Incidence and Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012. [http://globocan.iarc.fr]
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, Fu KK, Milas L. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7350–7356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous