Triticeae resources in Ensembl Plants
- PMID: 25432969
- PMCID: PMC4301745
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcu183
Triticeae resources in Ensembl Plants
Abstract
Recent developments in DNA sequencing have enabled the large and complex genomes of many crop species to be determined for the first time, even those previously intractable due to their polyploid nature. Indeed, over the course of the last 2 years, the genome sequences of several commercially important cereals, notably barley and bread wheat, have become available, as well as those of related wild species. While still incomplete, comparison with other, more completely assembled species suggests that coverage of genic regions is likely to be high. Ensembl Plants (http://plants.ensembl.org) is an integrative resource organizing, analyzing and visualizing genome-scale information for important crop and model plants. Available data include reference genome sequence, variant loci, gene models and functional annotation. For variant loci, individual and population genotypes, linkage information and, where available, phenotypic information are shown. Comparative analyses are performed on DNA and protein sequence alignments. The resulting genome alignments and gene trees, representing the implied evolutionary history of the gene family, are made available for visualization and analysis. Driven by the case of bread wheat, specific extensions to the analysis pipelines and web interface have recently been developed to support polyploid genomes. Data in Ensembl Plants is accessible through a genome browser incorporating various specialist interfaces for different data types, and through a variety of additional methods for programmatic access and data mining. These interfaces are consistent with those offered through the Ensembl interface for the genomes of non-plant species, including those of plant pathogens, pests and pollinators, facilitating the study of the plant in its environment.
Keywords: Comparative genomics; Functional genomics; Genetic variation; Genome browser; Transcriptomics; Triticeae.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists.
Figures
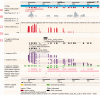


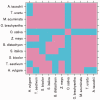


References
-
- Allen AM, Barker GLA, Berry ST, Coghill JA, Gwilliam R, Kirby S, Robinson P, et al. Transcript-specific, single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery and linkage analysis in hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011;9:1086–1099. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MD, Smith JB. Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 1991;334:309–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

