Synovial T cell hyporesponsiveness to myeloid dendritic cells is reversed by preventing PD-1/PD-L1 interactions
- PMID: 25433812
- PMCID: PMC4266919
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-014-0497-x
Synovial T cell hyporesponsiveness to myeloid dendritic cells is reversed by preventing PD-1/PD-L1 interactions
Abstract
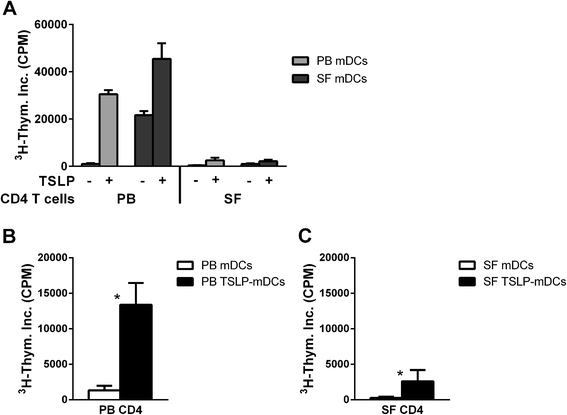
Introduction: The aim of this study was to investigate PD-1/PD-L1 involvement in the hyporesponsiveness of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid (SF) CD4 T cells upon stimulation by thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP)-primed CD1c myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs).
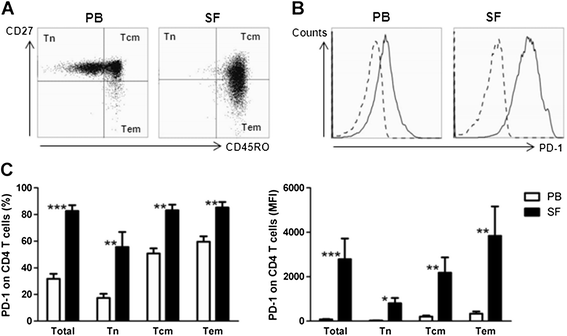
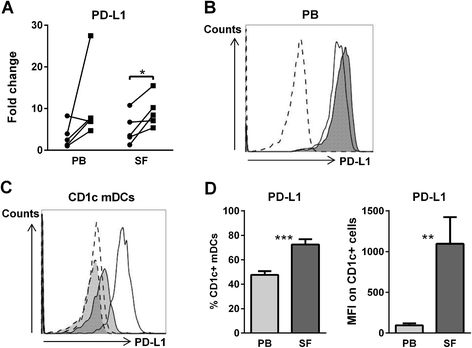
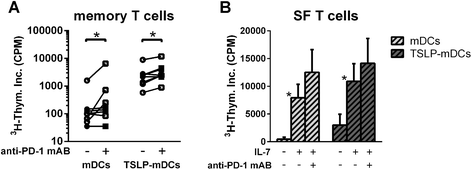
Methods: Expression of PD-1 on naïve (Tn), central memory (Tcm) and effector memory (Tem) CD4 T cell subsets was assessed by flow cytometry. PD-L1 expression and its regulation upon TSLP stimulation of mDCs from peripheral blood (PB) and SF of RA patients were investigated by quantitative RT-PCR and flow cytometry. The involvement of PD-1/PD-L1 interactions in SF T cell hyporesponsiveness upon (TSLP-primed) mDC activation was determined by cell culture in the presence of PD-1 blocking antibodies, with or without interleukin 7 (IL-7) as a recognized suppressor of PD-1 expression.
Results: PD-1 expression was increased on CD4 T cells derived from SF compared with PB of RA patients. TSLP increased PD-L1 mRNA expression in both PB and SF mDCs. PD-L1 protein expression was increased on SF mDCs compared with PB mDCs and was associated with T cell hyporesponsiveness. Blockade of PD-1, as well as IL-7 stimulation, during cocultures of memory T cells and (TSLP-primed) mDCs from RA patients significantly recovered T cell proliferation.
Conclusion: SF T cell hyporesponsiveness upon (TSLP-primed) mDC stimulation in RA joints is partially dependent on PD-1/PD-L1 interactions, as PD-1 and PD-L1 are both highly expressed on SF T cells and mDCs, respectively, and inhibiting PD-1 availability restores T cell proliferation. The potential of IL-7 to robustly reverse this hyporesponsiveness suggests that such proinflammatory cytokines in RA joints strongly contribute to memory T cell activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mechanism of dendritic cell-T cell crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Oct 5;25(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03159-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37798668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy of abatacept in reducing synovial T cell activation by CD1c myeloid dendritic cells is overruled by the stimulatory effects of T cell-activating cytokines.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Mar;67(3):637-44. doi: 10.1002/art.38982. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25469671
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, a novel proinflammatory mediator in rheumatoid arthritis that potently activates CD1c+ myeloid dendritic cells to attract and stimulate T cells.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1176-84. doi: 10.1002/art.38338. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24782181
-
Intra-articular CD1c-expressing myeloid dendritic cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients express a unique set of T cell-attracting chemokines and spontaneously induce Th1, Th17 and Th2 cell activity.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Oct 20;15(5):R155. doi: 10.1186/ar4338. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24286358 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial dendritic cells and T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;74:79-88. doi: 10.3109/03009748809102942. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988. PMID: 2976523 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Emerging phagocytosis checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Mar 7;8(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01365-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36882399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of dendritic cell-T cell crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Oct 5;25(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03159-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37798668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Moxibustion on PD-1/PD-L1-Related Molecular Expression and Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in RA Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 11;2021:6658946. doi: 10.1155/2021/6658946. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 39290616 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of PD-1 in the Autoimmune Response: Insights into Its Implication in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;25(14):7726. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147726. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Cancer: Regulation and Function of PD-L1 in Health and Immune-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8599. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158599. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morita Y, Yamamura M, Kawashima M, Harada S, Tsuji K, Shibuya K, Maruyama K, Makino H. Flow cytometric single-cell analysis of cytokine production by CD4+ T cells in synovial tissue and peripheral blood from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1669–1676. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1669::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-G. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cornelissen F, van Hamburg JP, Lubberts E. The IL-12/IL-23 axis and its role in Th17 cell development, pathology and plasticity in arthritis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:452–462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

