A large-scale cross-sectional study of ALK rearrangements and EGFR mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer in Chinese Han population
- PMID: 25434695
- PMCID: PMC4248273
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07268
A large-scale cross-sectional study of ALK rearrangements and EGFR mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer in Chinese Han population
Abstract
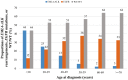
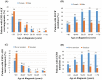
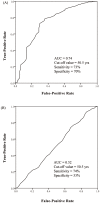
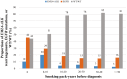
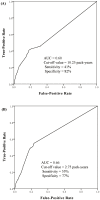
The predictive power of age at diagnosis and smoking history for ALK rearrangements and EGFR mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains not fully understood. In this cross-sectional study, 1160 NSCLC patients were prospectively enrolled and genotyped for EML4-ALK rearrangements and EGFR mutations. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to explore the association between clinicopathological features and these two genetic aberrations. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves methodology was applied to evaluate the predictive value. We showed that younger age at diagnosis was the only independent variable associated with EML4-ALK rearrangements (odds ratio (OR) per 5 years' increment, 0.68; p < 0.001), while lower tobacco exposure (OR per 5 pack-years' increment, 0.88; p < 0.001), adenocarcinoma (OR, 6.61; p < 0.001), and moderate to high differentiation (OR, 2.05; p < 0.001) were independently associated with EGFR mutations. Age at diagnosis was a very strong predictor of ALK rearrangements but poorly predicted EGFR mutations, while smoking pack-years may predict the presence of EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements but with rather limited power. These findings should assist clinicians in assessing the likelihood of EML4-ALK rearrangements and EGFR mutations and understanding their biological implications in NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Yes there is potential Competing Interest. Li Zhang has received research support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Lilly, and Roche. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R., Ma J., Zou Z. & Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64, 9–29 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T. et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 11, 121–128 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Rosell R. et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13, 239–246 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Wu Y. L. et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15, 213–222 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

