MR imaging near metallic implants using MAVRIC SL: initial clinical experience at 3T
- PMID: 25435186
- PMCID: PMC4323867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2014.09.010
MR imaging near metallic implants using MAVRIC SL: initial clinical experience at 3T
Abstract
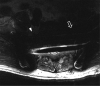
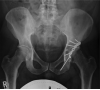
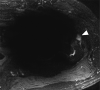
Rationale and objectives: To compare the effectiveness of multiacquisition with variable resonance image combination selective (MAVRIC SL) with conventional two-dimensional fast spin-echo (2D-FSE) magnetic resonance (MR) techniques at 3T in imaging patients with a variety of metallic implants.
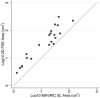
Materials and methods: Twenty-one 3T MR studies were obtained in 19 patients with different types of metal implants. Paired MAVRIC SL and 2D-FSE sequences were reviewed by two radiologists and compared for in-plane and through-plane metal artifact, visualization of the bone implant interface and surrounding soft tissues, blurring, and overall image quality using a two-tailed Wilcoxon signed rank test. The area of artifact on paired images was measured and compared using a paired Wilcoxon signed rank test. Changes in patient management resulting from MAVRIC SL imaging were documented.
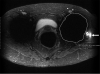
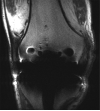
Results: Significantly less in-plane and through-plane artifact was seen with MAVRIC SL, with improved visualization of the bone-implant interface and surrounding soft tissues, and superior overall image quality (P = .0001). Increased blurring was seen with MAVRIC SL (P = .0016). MAVRIC SL significantly decreased the image artifact compared to 2D-FSE (P = .0001). Inclusion of MAVRIC SL to the imaging protocol determined the need for surgery or type of surgery in five patients and ruled out the need for surgery in 13 patients. In three patients, the area of interest was well seen on both MAVRIC SL and 2D-FSE images, so the addition of MAVRIC had no effect on patient management.
Conclusions: Imaging around metal implants with MAVRIC SL at 3T significantly improved image quality and decreased image artifact compared to conventional 2D-FSE imaging techniques and directly impacted patient management.
Keywords: MAVRIC SL; image quality; magnetic resonance imaging; metallic susceptibility artifact.
Copyright © 2015 AUR. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Metal artifact reduction with MAVRIC SL at 3-T MRI in patients with hip arthroplasty.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Jan;204(1):140-7. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11785. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 25539249 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro assessment of knee MRI in the presence of metal implants comparing MAVRIC-SL and conventional fast spin echo sequences at 1.5 and 3 T field strength.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 May;41(5):1291-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24668. Epub 2014 Jun 10. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 24912802 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated metallic artifact reduction imaging using spectral bin modulation of multiacquisition variable-resonance image combination selective imaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Oct;72:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.06.012. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32574683
-
MR Imaging with Metal-suppression Sequences for Evaluation of Total Joint Arthroplasty.Radiographics. 2016 Jan-Feb;36(1):209-25. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016150075. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Radiographics. 2016. PMID: 26587889 Review.
-
Advances in Metal Artifact Reduction Techniques for Periprosthetic Soft Tissue Imaging.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015 Sep;19(4):328-34. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1563734. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26583361 Review.
Cited by
-
Orthodontic appliances and MR image artefacts: An exploratory in vitro and in vivo study using 1.5-T and 3-T scanners.Imaging Sci Dent. 2021 Mar;51(1):63-71. doi: 10.5624/isd.20200199. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Imaging Sci Dent. 2021. PMID: 33828963 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Carbon Fiber Implants to Improve the Safety and Efficacy of Radiation Therapy for Spine Tumor Patients.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 14;15(2):199. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020199. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Volumetric and multispectral DWI near metallic implants using a non-linear phase Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill diffusion preparation.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Jun;87(6):2650-2666. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29153. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 35014729 Free PMC article.
-
Metallic Artifact Reduction of Multiacquisition With Variable Resonance Image Combination Selective-Short Tau Inversion Recovery for Postoperative Cervical Spine With Artificial Disk Replacement: A Preliminary Study.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2022 Mar-Apr 01;46(2):274-281. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001266. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2022. PMID: 35081602 Free PMC article.
-
What is the Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI for Component Loosening in THA?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Sep;477(9):2085-2094. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000772. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31135538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schenck JF. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med Phys. 1996 Jun;23(6):815–850. - PubMed
-
- Harris CA, White LM. Metal artifact reduction in musculoskeletal magnetic resonance imaging. Orthop Clin North Am. 2006 Jul;37(3):349–359. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

