Universal school-based prevention for illicit drug use
- PMID: 25435250
- PMCID: PMC6483627
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003020.pub3
Universal school-based prevention for illicit drug use
Abstract
Background: Drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease. Primary interventions should aim to reduce first use or to prevent the transition from experimental use to addiction. School is the appropriate setting for preventive interventions.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of universal school-based interventions in reducing drug use compared to usual curricular activities or no intervention.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group's Trials Register (September 2013), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (2013, Issue 9), PubMed (1966 to September 2013), EMBASE (1988 to September 2013) and other databases. We also contacted researchers in the field and checked reference lists of articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCT) evaluating school-based interventions designed to prevent illicit drugs use.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard methodological procedures expected by The Cochrane Collaboration.
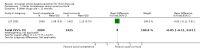
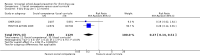
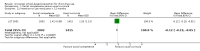
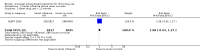
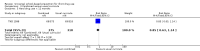
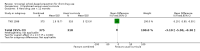
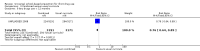
Main results: We included 51 studies, with 127,146 participants. Programmes were mainly delivered in sixth and seventh grade pupils. Most of the trials were conducted in the USA. Social competence approach versus usual curricula or no intervention Marijuana use at < 12 months follow-up: the results favoured the social competence intervention (risk ratio (RR) 0.90; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.81 to 1.01, four studies, 9456 participants, moderate quality evidence). Seven studies assessed this outcome (no data for meta-analysis): two showed a positive significant effect of intervention, three showed a non-significant effect, one found a significant effect in favour of the control group and one found a trend in favour of the control group.Marijuana use at 12+ months: the results favoured the social competence intervention (RR 0.86; 95% CI 0.74 to 1.00, one study, 2678 participants, high quality evidence). Seven studies assessed this outcome (no data for meta-analysis): two showed a significant positive effect of intervention, three showed a non-significant effect, one found a significant effect in favour of the control group and one a trend in favour of the control group.Hard drug use at < 12 months: we found no difference (RR 0.69; 95% CI 0.40 to 1.18, one study, 2090 participants, moderate quality evidence). Two studies assessed this outcome (no data for meta-analysis): one showed comparable results for the intervention and control group; one found a statistically non-significant trend in favour of the social competence approach.Hard drug use at 12+ months: we found no difference (mean difference (MD) -0.01; 95% CI -0.06 to 0.04), one study, 1075 participants, high quality evidence). One study with no data for meta-analysis showed comparable results for the intervention and control group.Any drug use at < 12 months: the results favoured social competence interventions (RR 0.27; 95% CI 0.14 to 0.51, two studies, 2512 participants, moderate quality evidence). One study with 1566 participants provided continuous data showing no difference (MD 0.02; 95% CI -0.05 to 0.09, moderate quality evidence). Social influence approach versus usual curricula or no intervention Marijuana use at < 12 months: we found a nearly statistically significant effect in favour of the social influence approach (RR 0.88; 95% CI 0.72 to 1.07, three studies, 10,716 participants, moderate quality evidence). One study with 764 participants provided continuous data showing results that favoured the social influence intervention (MD -0.26; 95% CI -0.48 to -0.04).Marijuana use at 12+ months: we found no difference (RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.81 to 1.13, one study, 5862 participants, moderate quality evidence). One study with 764 participants provided continuous data and showed nearly statistically significant results in favour of the social influence intervention (MD -0.22; 95% CI -0.46 to 0.02). Of the four studies not providing data for meta-analysis a statistically significant protective effect was only found by one study.Hard drug use at 12+ months: one study not providing data for meta-analysis found a significant protective effect of the social influence approach.Any drug use: no studies assessed this outcome. Combined approach versus usual curricula or no intervention Marijuana use at < 12 months: there was a trend in favour of intervention (RR 0.79; 95% CI 0.59 to 1.05, three studies, 8701 participants, moderate quality evidence). One study with 693 participants provided continuous data and showed no difference (MD -1.90; 95% CI -5.83 to 2.03).Marijuana use at 12+ months: the results favoured combined intervention (RR 0.83; 95% CI 0.69 to 0.99, six studies, 26,910 participants, moderate quality evidence). One study with 690 participants provided continuous data and showed no difference (MD -0.80; 95% CI -4.39 to 2.79). Two studies not providing data for meta-analysis did not find a significant effect.Hard drug use at < 12 months: one study with 693 participants provided both dichotomous and continuous data and showed conflicting results: no difference for dichotomous outcomes (RR 0.85; 95% CI 0.63 to 1.14), but results in favour of the combined intervention for the continuous outcome (MD -3.10; 95% CI -5.90 to -0.30). The quality of evidence was high.Hard drug use at 12+ months: we found no difference (RR 0.86; 95% CI 0.39 to 1.90, two studies, 1066 participants, high quality evidence). One study with 690 participants provided continuous data and showed no difference (MD 0.30; 95% CI -1.36 to 1.96). Two studies not providing data for meta-analysis showed a significant effect of treatment.Any drug use at < 12 months: the results favoured combined intervention (RR 0.76; 95% CI 0.64 to 0.89, one study, 6362 participants).Only one study assessed the effect of a knowledge-focused intervention on drug use and found no effect. The types of comparisons and the programmes assessed in the other two groups of studies were very heterogeneous and difficult to synthesise.
Authors' conclusions: School programmes based on a combination of social competence and social influence approaches showed, on average, small but consistent protective effects in preventing drug use, even if some outcomes did not show statistical significance. Some programmes based on the social competence approach also showed protective effects for some outcomes.Since the effects of school-based programmes are small, they should form part of more comprehensive strategies for drug use prevention in order to achieve a population-level impact.
Conflict of interest statement
FF is an author of an included study (UNPLUGGED 2008). He did not participate in the evaluation of and data extraction for the related papers.
SM EV,DB have no conflicts of interest
Figures

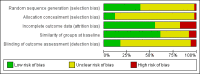




























Update of
-
School-based prevention for illicit drugs' use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD003020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD003020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003020.pub3. PMID: 15846647 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
ADM 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gersick KE, Grady K, Snow DL. Social‐cognitive skill development with sixth graders and its initial impact on substance use. Journal of Drug Education 1988;18(1):55‐70. - PubMed
-
- Snow DL, Tebes JK, Arthur MW, Tapasak RC. Two‐year follow‐up of a social‐cognitive intervention to prevent substance use. Journal of Drug Education 1992;22(2):101‐14. - PubMed
ALERT 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bell RM, Ellickson PL, Harrison ER. Do drug prevention effects persist into high school? How Project ALERT did with ninth graders. Preventive Medicine 1993;22:463‐83. - PubMed
-
- Ellickson PL, Bell RM. Drug prevention in junior high: a multi‐site longitudinal test. Science 1990;247:1299‐305. - PubMed
-
- Ellickson PL, Bell RM, Harrison ER. Changing adolescent propensities to use drugs: results from Project ALERT. Health Education Quarterly 1993;20(2):227‐42. - PubMed
ALERT 2003 {published data only}
ALERT 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pierr TL, Osggd SW, Mincemoyer CC, Kaltreider DL, Kauh TJ. Results of an independent evaluation of project ALERT delivered in schools by cooperative extension. Prevention Science 2005;6(4):305‐17. - PubMed
ALERT 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ringwalt CL, Clark HK, Hanley S, Shamblen SR, Flewelling RL. Project ALERT: a cluster randomised trial. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2009;163(7):625‐32. - PubMed
-
- Ringwalt CL, Clark HK, Hanley S, Shambles SR, Flewelling RL. The effect of project ALERT one year past curriculum completion. Prevention Science 2010;11:172‐84. - PubMed
ASAP 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bernstein E, Woodal WG. Changing perceptions of riskiness in drinking, drugs and driving: an emergency department‐based alcohol and substance abuse prevention program. Annals of Emergency Medicine 1987;16(12):1350‐4. - PubMed
ATD 2010 {published data only}
-
- Copeland AL, Williamson DA, Kendzor DA, Bisinelle MS, Rash CJ, Kulesza M, et al. A school based alcohol, tobacco, and drug prevention program for children: the Wise Mind study. Cognitive Therapy and Research 2010;34:522‐32.
CLIMATE 2009 {published data only}
-
- Newton NC, Andrews G, Teeson M, Vogl LE. Delivering prevention for alcohol and cannabis using the internet: a cluster randomised controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2009;48:579‐84. - PubMed
-
- Newton NC, Teeson M, Vogl LE, Andrews G. Internet based prevention for alcohol and cannabis use: final results of the Climate Schools course. Addiction 2009;105:749‐59. - PubMed
CMER 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guo R, He Q, Shi J, Gong J, Wang H, Wang Z. Short term impact of cognition motivation emotional intelligence resistance skills program on drug use prevention for school students in Wuhan, China. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology 2010;30(6):720‐5. - PubMed
CROSS AGE TUT 1985 {published data only}
-
- Malvin JH, Moskovitz JM, Schaps E, Schaeffer GA. Evaluation of two school‐based alternatives programs. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 1985;30(3):98‐108.
DARE 1991 {published data only}
-
- Clayton RR, Cattarello A, Walden KP. Sensation seeking as a potential mediating variable for school‐based prevention intervention. A two‐year follow‐up of DARE. Health Communication 1991;3(4):229‐39.
-
- Clayton RR, Cattarello AM, Johnstone BM. The effectiveness or Drug Abuse Resistance Education (project DARE): 5‐year follow‐up results. Preventive Medicine 1996;25:307‐18. - PubMed
-
- Lynam DR, Milich R, Zimmerman R, Novak SP, Logan TK, Martin C, et al. Project DARE: no effects at 10‐year follow‐up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999;67(4):590‐3. - PubMed
DARE 1991 B {published data only}
-
- Ringwalt C, Ennett ST, Holt KD. An outcome evaluation of Project DARE (Drug Abuse Resistance Education). Health Education Research 1991;6(3):327‐37.
DARE 2003 {published data only}
-
- Perry CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortensem S, Bosma LM, Farbakhsh K, Munson KA, et al. A randomised controlled trial of the middle and junior high school DARE and DARE plus program. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157:178‐84. - PubMed
DRS 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hecht ML, Corman SR, Miller‐Rassulo M. An evaluation of the Drug Resistance Project: a comparison of film versus live performance media. Health Communication 1993;5(2):75‐88.
GATEHOUSE 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bond L, Thomas L, Coffey C, Glover S, Butler H, Carlin JB, et al. Long term impact of the Gatehouse Project in cannabis use of 16 year olds in Australia. Journal of School Health 2004;74(1):23‐9. - PubMed
GOOD BEHAVIOR GAME 2004 {published data only}
-
- Furr‐Holden CDM, Ialongo NS, Anthony JC, Petras H, Kellam SG. Developmentally inspired drug prevention: middle school outcomes in a school‐based randomised prevention trial. Drug Alcohol Dependence 2004;73:149‐58. - PubMed
GOOD BEHAVIOR GAME 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kellam SG, Wang W, Mackenzie ACL, Brown CH, Ompad DC, Or F, et al. The impact of the Good Behavior Game, a universal classroom‐based preventive intervention in first and second grades, on high‐risk sexual behaviors and drug abuse and dependence disorders into young adulthood. Prevention Science 2014;15(Suppl 1):PS6‐18. - PMC - PubMed
KACM 1991 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Young M, Clark M, Garrett C, Hooks S, Kersten C. Effects of a take‐home drug prevention program on drug‐related communication and beliefs of parents and children. Journal of School Health 1991;61(8):346‐50. - PubMed
KEEPIN' IT REAL 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hecht ML, Marsiglia FF, Elek E, Wagstaff DA, Kulis S, Dustman P, et al. Culturally grounded substance use prevention: an evaluation of the keepin’ it R.E.A.L. Curriculum. Prevention Science 2003;4(4):233‐48. - PubMed
KEEPIN' IT REAL 2008 {published data only}
KEEPIN' IT REAL 2010 {published data only}
-
- Elek E, Wagstaff DA, Hecht ML. Effects of the 5th and 7th grade enhanced versions of the keepin' it REAL substance use prevention curriculum. Journal of Drug Education 2010;40(1):61‐79. - PubMed
LST 1984 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Baker E, Filazzola AD, Botvin EM. A cognitive‐behavioral approach to substance abuse prevention: one‐year follow‐up. Addictive Behaviors 1990;15:47‐63. - PubMed
-
- Botvin GJ, Baker E, Renick NL, Filazzola AD, Botvin EM. A cognitive‐behavioral approach to substance abuse prevention. Addictive Behaviors 1984;9:137‐47. - PubMed
LST 1990 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Baker E, Dusenbury L, Botvin EM, Diaz T. Long‐term follow‐up results of a randomised drug abuse prevention trial in a white middle‐class population. JAMA 1995;273(14):1106‐12. - PubMed
-
- Botvin GJ, Baker E, Dusennbury L, Tortu S, Botvin EM. Preventing adolescent drug abuse through a multimodal cognitive‐behavioral approach: results of a 3‐year study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(4):437‐46. - PubMed
LST 1994 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Schinke SP, Epstein JA, Diaz T. Effectiveness of culturally focused and generic skills training approaches to alcohol and drug abuse prevention among minority youths. Psychology Addictive Behaviors 1994;8(2):116‐27.
-
- Botvin GJ, Schinke SP, Epstein JA, Diaz T, Botvin EM. Effectiveness of culturally focused and generic skills training approaches to alcohol and drug abuse prevention among minority adolescents: two‐year follow‐up results. Psychology Addictive Behaviors 1995;9(3):183‐94.
LST 2001 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Griffin KW, Diaz T, Ifill‐Williams M. Drug abuse prevention among minority adolescents: posttest and one‐year follow‐up of a school‐based preventive intervention. Prevention Science 2001;2(1):1‐13. - PubMed
LST 2006 {published data only}
-
- Seal N. Preventing tobacco and drug use among Thai high school students through life skill training. Nursing and Health Sciences 2006;8:164‐8. - PubMed
LST and KEPT LEFT 2008 {published data only}
-
- Resnicow K, Reddy SP, James S, Gabebodeen Omardien R, Kambaran NS, Langner HG, et al. Comparison of two smoking prevention programs among South Africa high school students: results of a randomised trial. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 2008;36:231‐43. - PubMed
MOTIVATIONAL INTERV 2011 {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Hunt C, Jenkins RJ, Strang J. Cluster randomised trial of the effectiveness of motivational interviewing for universal prevention. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2011;114:177‐84. - PubMed
NAPA 1984 {published data only}
-
- Moskowitz JM, Malvin JH, Schaeffer GA, Schaps E. An experimental evaluation of a drug education course. Journal of Drug Education 1984;14(1):9‐22. - PubMed
PATHS 2012 {published data only}
PAY 1984 {published data only}
-
- Cook R, Lawrence H, Morse C, Roehl J. An evaluation of the alternatives approach to drug abuse prevention. International Journal of the Addictions 1984;19(7):767‐87. - PubMed
POSITIVE ACTION 2009 {published data only}
PROJECT ACTIVE 2011 {published data only}
PROJECT CHARLIE 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hurry J, McGurk H. An evaluation of a primary prevention programme for schools. Addiction Research 1997;5(1):23‐38.
PROJECT SPORT 2005 {published data only}
-
- Werch C, Moore MJ, DiClemente CC, Bledsoe R, Jobli E. A multihealth behavioral intervention integrating physical activity and substance use prevention for adolescents. Prevention Science 2005;6(3):213‐25. - PubMed
REHEARSAL PLUS 1990 {published data only}
-
- Jones RT, McDonald DW, Fiore MF, Arrington T, Randall J. A primary preventive approach to children's drug refusal behavior: the impact of Rehearsal‐Plus. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1990;15(2):211‐23. - PubMed
REHEARSAL PLUS 1993 {published data only}
-
- Corbin SKT, Jones RT, Schulman RS. Drug refusal behavior: the relative efficacy of skill‐based treatment. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1993;18(6):769‐84. - PubMed
REHEARSAL PLUS 1995 {published data only}
-
- Jones RT, Corbin SKT, Sheehy L, Bruce S. Substance refusal: more than "Just Say No". Journal of Child Adolescent Substance Abuse 1995;4(2):1‐26.
Sexter 1984 {published data only}
-
- Sexter J, Sullivan AP, Wepner SF, Denmark R. Substance abuse: assessment of the outcomes of activities and activity clusters in school‐based prevention. International Journal of the Addictions 1984;19(1):79‐92. - PubMed
Sigelman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sigelman CK, Bridges LJ, Leach DB, Mack KL, Rinehart CS, Sorongon AG, et al. The efficacy of an education program to teach children a scientific theory of how drugs affect behavior. Applied Developmental Psychology 2003;24:573‐93.
SKILLS FOR ADOL 2002 {published data only}
-
- Eisen M, Zellman GL, Massett HA, Muray DM. Evaluating the Lions‐Quest "Skills for Adolescence" drug education program: first year behavior outcomes. Addictive Behaviors 2002;27:619‐32. - PubMed
-
- Eisen M, Zellmanb GL, Murray DL. Evaluating the Lions‐Quest “Skills for Adolescence” drug education program: second‐year behavior outcomes. Addictive Behaviors 2003;28:883‐97. - PubMed
SMART 1988 {published data only}
-
- Hansen WB, Anderson Johnson C, Flay BR, Graham JW, Sobel J. Affective and social influences approaches to the prevention of multiple substance abuse among seventh grade students: results from project SMART. Preventive Medicine 1988;17:135‐54. - PubMed
SMART 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hansen WB, Graham JW. Preventing alcohol, marijuana and cigarette use among adolescents: peer pressure resistance training versus establishing conservative norms. Preventive Medicine 1991;20:414‐30. - PubMed
-
- Palmer RF, Graham JW, White EL, Hansen WB. Applying multilevel analytic strategies in adolescent substance use prevention research. Preventive Medicine 1998;27:328‐36. - PubMed
TCYL 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sloboda Z, Stephens P, Pyakuryal A, Teasdale B, Stephens RC, Hawtorne RD, et al. Implementation fidelity: the experience of the adolescent substance prevention study. Health Education Research 2009;24(3):394‐406. - PubMed
-
- Sloboda Z, Stephens RC, Stephens PC, Grey SF, Teasdale B, Hawtorne RD, et al. The adolescent substance abuse prevention study: a randomised field trial of a universal substance abuse prevention program. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2009;102:1‐10. - PubMed
THINK SMART 2009 {published data only}
TND 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sun W, Skara S, Sun P, Dent CW, Sussman S. Project Toward No Drug Abuse: long term substance use outcomes evaluation. Prevention Medicine 2006;42:188‐92. - PubMed
-
- Sussman S, Dent CW, Stacy AW. Project Towards No Drug Abuse: a review of the findings and future directions. American Journal of Health Behavior 2002;26(5):354‐65. - PubMed
-
- Sussman S, Dent CW, Stacy AW, Craig S. One‐year outcomes of project Towards No Drug Abuse. Preventive Medicine 1998;27:632‐42. - PubMed
TND 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dent CW, Sussman S, Stacy AW. Project Towards No Drug Abuse: generalizability to a general high school sample. Preventive Medicine 2001;32:514‐20. - PubMed
TND 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sussman S, Dent CW, Craig S, Ritt‐Olsen A, McCuller WJ. Development and immediate impact of a self‐instruction curriculum for an adolescent indicated drug abuse prevention trial. Journal of Drug Education 2002;32(2):121‐37. - PubMed
-
- Sussman S, Sun P, McCuller WJ, Dent CW. Project towards no drug abuse: two‐year outcomes of a trial that compares health educator delivery to self‐instruction. Preventive Medicine 2003;37:155‐62. - PubMed
TND 2008 {published data only}
UNPLUGGED 2008 {published data only}
-
- Faggiano F, Galanti MR, Bohrn K, Burkhart G, Vigna‐Taglianti F, Cuomo L, et al. The effectiveness of a school based substance abuse prevention program: EU‐DAP cluster randomised controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2008;47:537‐43. - PubMed
-
- Faggiano F, Richardson C, Bohrn K, Galanti MR. EU‐DAp Study Group. A cluster randomized controlled trial of school based prevention of tobacco, alcohol and drug use: The EU‐Dap design and study population. Preventive Medicine 2007;44:170‐3. - PubMed
-
- Faggiano F, Vigna‐Taglianti F, Burchart G, Bohrn K, Cuomo L, Gregori D, et al. The effectiveness of a school based substance abuse prevention program: 18 months follow up of the EU‐DAP cluster randomised controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2010;118:56‐64. - PubMed
-
- Vigna‐Taglianti F, Vandrucci S, Faggiano F, Buckhart G, Galanti MR, the EU‐DAP Study Group. Is universal prevention against youths' substance misuse really universal? Gender specific effects in the EU‐DAP school based prevention trial. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2009;63:722‐8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ambtman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ambtman R, Madak P, Koss D, Strople MJ. Evaluation of a comprehensive elementary school curriculum‐based drug education program. Journal of Drug Education 1990;20(3):199‐25. - PubMed
Amirian 2012 {published data only}
-
- Amirian K, Shafiei Amiri M. Effectiveness of education and life skills approach to publishing information on the prevention of addiction in the first year of high school students. European Psychiatry 2012;27 Suppl 1:1.
Amundsen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Amundsen EJ, Ravndal E. Does successful school‐based prevention of bullying influence substance use among 13‐ to 16‐year‐olds?. Drugs: Education, Prevention and Policy 2010;17(1):42‐54.
Battistich 1996 {published data only}
-
- Battistich V, Schaps E, Watson M, Solomon D. Prevention effects of the child development project: early findings from an ongoing multisite demonstration trial. Journal of Adolescent Research 1996;11(1):12‐35.
Becker 1992 {published data only}
-
- Becker HK, Agopian MW, Yeh S. Impact evaluation of drug abuse resistance education (DARE). Journal of Drug Education 1992;22(4):283‐91. - PubMed
Bernett 2012 {published data only}
Blum 1978 {published data only}
-
- Blum RH, Garfield EF, Johnstone JL, Magistad JD. Drug education: further results and recommendations. Journal of Drug Issues 1978;8(4):379‐426.
Bonaguro 1988 {published data only}
-
- Bonaguro JA, Rhonehouse M, Bonaguro EW. Effectiveness of four school health education projects upon substance use, self‐esteem, and adolescent stress. Health Education Quarterly 1988;15(1):81‐92. - PubMed
Botvin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Epstein JA, Baker E, Diaz T, Ifill‐Williams M. School‐based drug abuse prevention with inner‐city minority youth. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse 1997;6(1):5‐19.
Botvin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Botvin GJ, Griffin KW, Diaz T, Scheier LM, Williams C, Epstein JA. Preventing illicit drug use in adolescents: long‐term follow‐up data from a randomised control trial of a school population. Addictive Behaviors 2000;25(5):769‐74. - PubMed
Bry 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bry BH. Reducing the incidence of adolescent problems through preventive intervention: one and five‐year follow‐up. American Journal of Community Psychology 1982;10(3):265‐76. - PubMed
Calafat 1984 {published data only}
-
- Calafat A, Amengual M, Farres C, Monserrat M. Efficacy of a prevention programme on the drugs, especially on "take decisions", for specialists or professors [Eficacia de un programa de prevencion sobre drogas, especialmente centrado en la "toma de decisiones", segun sea desarrolado por especialistas o por profesores de los alumnos]. Addiciones 1984;IX(3):147‐69.
Calafat 1989 {published data only}
-
- Calafat A, Amengual M, Mejias G, Borras M, Palmer A. Valuation of the school based prevention programme "You decide" [Evaluacion del programa de prevencion escolar "Tu decides"]. Addiciones 1989;1(2):96‐111.
Calafat 1995 {published data only}
-
- Calafat A, Amengual M, Guimerans C, Rodriguez‐Martos A, Ruiz R. "You decide" 10 years of a school based prevention programme ["Tu decides": 10 anos de un programa de prevencion escolar]. Addiciones 1995;7(4):509‐26.
Clark 2011a {published data only}
-
- Clark HK, Ringwalt CL, Shamblen SR, Hanley SM. Project success' effects on substance use‐related attitudes and behaviors: a randomized controlled trial in alternative high schools. Journal of Drug Education 2011;41(1):17‐44. - PubMed
Clark 2011b {published data only}
-
- Clark HK, Ringwalt CL, Shamblen SR, Hanley SM, Flewelling RL. Are substance use prevention programs more effective in schools making adequate yearly progress? A study of Project ALERT. Journal of Drug Education 2011;41(3):271‐88. - PubMed
Colnes 2001 {published data only}
-
- Colnes RM. The effectiveness of a school‐based substance use prevention program. Dissertations and Theses 2000.
Connell 1986 {published data only}
-
- Connell DB, Turner RR, Mason EF, Olsen LK. School health education evaluation. International Journal of Educational Research 1986;10:245‐345.
Conrod 2012 {published data only}
-
- Conrod PJ, O'Leary‐Barrett M, Pihl R, Peterson J, Seguin J, Masse B. A cluster RCT investigating the effects of delaying onset of substance use on adolescent cognitive development and substance use disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:350A.
Cuijpers 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cuijpers P, Jonkers R, Weerdt I, Jong A. The effects of drug abuse prevention at school: the "Healthy School and Drugs" project. Addiction 2002;97:67‐73. - PubMed
D'Amico 2002 {published data only}
-
- D'Amico EJ, Fromme K. Brief prevention for adolescent risk‐taking behavior. Addiction 2002;97(5):563‐74. - PubMed
Dedobbeleer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dedobbeleer N, Desjardins S. Outcomes of an ecological and participatory approach to prevent alcohol and other drug abuse among multiethnic adolescents. Substance Use Misuse 2001;36(13):1959‐91. - PubMed
De Jong 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jong W. A short‐term evaluation of project DARE (Drug Abuse Resistance Education): preliminary indications of effectiveness. Journal of Drug Education 1987;17(4):279‐94. - PubMed
De La Rosa 1995 {published data only}
-
- Rosa Lopez A. La Prevencion de las Drogodependencias en el Ambito Escolar. Una Experiencia Pratica Evaluada [Thesis for Degree in Psychology]. Barcelona: Universitat de Barcelona, 1995.
Dent 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dent CW, Sussman S, Hennesy M, Galaif ER, Stacy AW, Moss MA, et al. Implementation and process evaluation of a school‐based drug abuse prevention program: project towards no drug abuse. Journal of Drug Education 1998;28(4):361‐75. - PubMed
DeWit 2000 {published data only}
-
- DeWit DJ, Steep B, Silverman G, Stevens‐Lavigne A, Ellis K, Smythe C, et al. Evaluating an in‐school drug prevention program for at‐risk youth. Alberta Journal of Educational Research 2000;46(2):117‐33.
Donaldson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Donaldson SI, Graham JW, Hansen WB. Testing the generalizability of intervening mechanism theories: understanding the effects of adolescent drug use prevention interventions. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1994;17(2):195‐216. - PubMed
Dukes 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dukes RL, Stein JA, Ullman JB. Long‐term impact of drug abuse resistance education (DARE). Evaluation Review 1997;21(4):483‐500. - PubMed
-
- Dukes RL, Ullman JB, Stein JA. Three‐year follow‐up of a drug abuse resistance education (D.A.R.E.). Evaluation Review 1996;20(1):49‐66. - PubMed
-
- Dukes RL, Ulman JB, Stein JA. An evaluation of D.A.R.E. (Drug Abuse Resistance Education), using a Solomon four‐group design with latent variables. Evaluation Review 1995;19(4):409‐35.
Duncan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Duncan TE, Duncan SC, Beauchamp N, Wells J, Ary DV. Development and evaluation of an interactive CD‐ROM refusal skills program to prevent youth substance use: "Refuse to use". Journal of Behavioral Medicine 2000;23(1):59‐72. - PubMed
Dupont 1984 {published data only}
-
- Dupont PJ, Jason LA. Assertiveness training in a preventive drug education program. Journal of Drug Education 1984;14(4):369‐78. - PubMed
Eggert 1990 {published data only}
-
- Eggert LL, Seyl CD, Nicholas LJ. Effects of a school‐based prevention program for potential high school dropouts and drug abusers. International Journal of the Addictions 1990;25(7):773‐801. - PubMed
Eggert 1994 {published data only}
-
- Eggert LL, Thompson EA, Herting JR, Nicholas LJ, Dicker BG. Preventing adolescent drug abuse and high‐school drop out through an intensive school‐based social network development program. American Journal of Health Promotion 1994;8(3):202‐15. - PubMed
-
- Thompson EA, Horn M, Herting JR, Eggert LL. Enhancing outcomes in an indicated drug prevention program for high‐risk youth. Journal of Drug Education 1997;27(1):19‐41. - PubMed
Elliot 2012 {published data only}
-
- Elliott JC, Carey KB. Correcting exaggerated marijuana use norms among college abstainers: a preliminary test of a preventive intervention. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2012;73(6):976‐80. - PubMed
Errecart 1991 {published data only}
-
- Errecart MT, Walberg HJ, Ross JG, Gold RS, Fiedler JL, Kolbe LJ. Effectiveness of teenage health teaching modules. Journal of School Health 1991;61(1):26‐30. - PubMed
Fraguela 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fraguela JAG, Martin AL, Trinanes ER. Drug abuse prevention in the school: four years follow‐up of a program. Psicothema 2002;14(4):685‐92.
-
- Fraguela JAG, Martin AL, Trinanes ER. Drug‐abuse prevention in the school: four year follow‐up of a programme. Psychology in Spain 2003;7(1):29‐38.
Freimuth 1997 {published data only}
-
- Freimuth VS, Plotnick CA, Ryan CE, Schiller S. Right turns only: an evaluation of a video‐based, multicultural drug education series for seventh graders. Health Education Behavior 1997;24(5):555‐67. - PubMed
Ghosh‐Dastidar 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ghosh‐Dastidar B, Longshore DL, Ellickson PL, McCaffrey DF. Modifying pro‐drug risk factors in adolescents: results from project ALERT. Health Education and Behavior 2004;31(3):318‐34. - PubMed
Gilchrist 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gilchrist LD, Schinke SP, Trimble JE, Cvetkovich GT. Skills enhancement to prevent substance abuse among American Indian adolescents. International Journal of the Addictions 1987;22(9):869‐79. - PubMed
Giles 2010 {published data only}
-
- Giles SM, Pankratz MM, Ringwalt C, Hansen WB, Dusenbury L, Jackson‐Newsom J. Teachers’ delivery skills and substance use prevention program outcomes: the moderating role of students’ need for cognition and impulse decision making. Journal of Drug Education 2010;40(4):395‐410. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1990 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez GM. Effects of a theory‐based, peer‐focused drug education course. Journal of Counseling and Development 1990;68(4):446‐9.
Graham 1990 {published data only}
-
- Graham JW, Johnson CA, Hansen WB, Flay BR, Gee M. Drug use prevention programs, gender, and ethnicity: evaluation of three seventh‐grade project SMART cohorts. Preventive Medicine 1990;19:305‐13. - PubMed
Green 1989 {published data only}
-
- Green JJ, Kelley JM. Evaluating the effectiveness of a school drug and alcohol prevention curriculum: a new look at "Here's looking at you, two". Journal of Drug Education 1989;19(2):117‐32. - PubMed
Griffin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Griffin KW, Botvin GJ, Nichols TR, Doyle MM. Effectiveness of a universal drug abuse prevention approach for youth at high risk for substance use initiation. Preventive Medicine 2003;36:1‐7. - PubMed
Haaga 2011 {published data only}
Hansen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hansen W, McNeal RB. How DARE works: an examination of program effects on mediating variables. Health Education & Behavior 1997;24(2):165‐76. - PubMed
Hansen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hansen WB, Dusenbury L. All Stars Plus: a competence and motivation enhancement approach to prevention. Health Education 2004;104(6):371‐81.
Hansen 2011 {published data only}
Harmon 1993 {published data only}
-
- Harmon MA. Reducing the risk of drug involvement among early adolescents. An evaluation of Drug Abuse Resistance Education (DARE). Evaluation Review 1993;17(2):221‐39.
Harrington 2001 {published data only}
-
- Harrington NG, Giles SM, Hoyle RH, Feeney G, Yungbluth SC. Evaluation of the All Stars character education and problem behavior prevention program: effects on mediator and outcome variables for middle school students. Health Education & Behavior 2001;28(5):533‐46. - PubMed
Huang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Huang CM, Chien LY, Cheng CF, Guo JL. Integrating life skills into a theory‐based drug‐use prevention program: effectiveness among junior high students in Taiwan. Journal of School Health 2012;82(7):328‐35. - PubMed
Kim 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kim S. An evaluation of Ombudsman primary prevention program on student drug abuse. Journal of Drug Education 1981;11(1):27‐36.
Kim 1982 {published data only}
-
- Kim S. Feeder area approach: an impact evaluation of a prevention project on student drug abuse. International Journal of the Addictions 1982;17(2):305‐13. - PubMed
Kim 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kim S, McLeod JH, Shantzis C. An outcome evaluation of refusal skills program as a drug abuse prevention strategy. Journal of Drug Education 1989;19(4):363‐71. - PubMed
Kim 1993 {published data only}
-
- Kim S, McLeod JH, Shantzis C. An outcome evaluation of here's looking at you 2000. Journal of Drug Education 1993;23(1):67‐81. - PubMed
Komro 2013 {published data only}
-
- Komro KA, Wagenaar AC, Boyd ML, et al. Prevention trial in the Cherokee nation: Research and intervention design. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:209A.
Kovach Clark 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kovach Clark H, Ringwalt CL, Hanley S, Shamblen SR. Project ALERT’s effects on adolescents’ prodrug beliefs: a replication and extension study. Health Education & Behavior 2010;37(3):357‐76. - PubMed
Kreutter 1991 {published data only}
-
- Kreutter KJ, Gewirtz H, Davenny JE, Love C. Drug and alcohol prevention project for sixth‐graders: first‐year findings. Adolescence 1991;26(102):287‐92. - PubMed
Lewis 1972 {published data only}
-
- Lewis JM, Gossett JT, Phillips VA. Evaluation of a drug prevention program. Hospital Community Psychiatry 1972;23(4):124‐6. - PubMed
Lisha 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lisha NE, Sun P, Rohrbach LA, Spruijt‐Metz D, Unger JB, Sussman S. An evaluation of immediate outcomes and fidelity of a drug abuse prevention program in continuation high schools: project towards no drug abuse (TND). Journal of Drug Education 2012;42(1):33‐57. - PubMed
Longshore 2007 {published data only}
-
- Longshore D, Ellickson PL, McCaffrey DF, Clair PA. School based drug prevention among at risk adolescent: Effect of ALERT Plus. Health Education & Behavior 2007;34(4):651‐68. - PubMed
LoSciuto 1988 {published data only}
-
- LoSciuto L, Ausetts MA. Evaluation of a drug abuse prevention program: a field experiment. Addictive Behaviors 1988;13:337‐51. - PubMed
McAlister 1980 {published data only}
Menrath 2012 {published data only}
-
- Menrath I, Mueller‐Godeffroy E, Pruessmann C, Ravens‐Sieberer U, Ottova V, Pruessmann M, et al. Evaluation of school‐based life skills programmes in a high‐risk sample: a controlled longitudinal multi‐centre study. Journal of Public Health 2012;20:159–70.
Moberg 1990 {published data only}
-
- Moberg DP, Piper DL. An outcome evaluation of Project Model Health: a middle school health promotion program. Health Education Quarterly 1990;17(1):37‐51. - PubMed
Moon Hopson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Moon Hopson L. Effectiveness of culturally grounded adaptations of an evidence‐based substance abuse prevention program with alternative school students. Dissertation and Thesis. In: UMI. University of Texas at Austin, 2006.
Moskowitz 1983 {published data only}
-
- Malvin J, Moskovitz JM, Schaeffer GA, Schaps E. Teacher training in affective education for the primary prevention of adolescent drug abuse. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1984;10(2):223‐35. - PubMed
-
- Moskovitz JM, Malvin J, Schaeffer GA, Schaps E. Evaluation of a junior high school primary prevention program. Addictive Behaviors 1983;8:393‐401. - PubMed
-
- Moskovitz JM, Schaps E, Schaeffer GA, Malvin JH. Evaluation of a substance abuse prevention program for junior high school students. International Journal of the Addictions 1984;19(4):419‐30. - PubMed
Nasir 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nasir M. Peer education is very effective in promotion of knowledge and attitude of high school students about HIV/AIDS/STIS in Bahawalpur, Pakistan. Journal of Sexual Medicine 2011;8:204.
Nozu 2006 {published data only}
O'Donnell 1995 {published data only}
-
- O'Donnell J, Hawkins JD, Catalano RF, Abbott RD, Day LE. Preventing school failure, drug use, and delinquency among low‐income children: long‐term intervention in elementary schools. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1995;65(1):87‐100. - PubMed
O'Leary‐Barrett 2011a {published data only}
-
- O’Leary‐Barrett M, Topper L, Mackie CJ, Castellanos‐Ryan N, Al‐Khudhairy N, Conrod PJ. The adventure RCT: Effective delivery of personality‐targeted interventions for substance misuse by educational professionals. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35:316A.
O'Leary‐Barrett 2011b {published data only}
-
- O'Leary‐Barrett M, Topper L, MacKie CJ, Castellanos‐Ryan N, Al‐Khudhairy N, Conrod PJ. The adventure RCT: Effective delivery of personality‐targeted interventions for substance misuse by educational professionals. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35:316A.
O'Neill 2011 {published data only}
-
- O'neill JM, Clark JK, Jones JA. Promoting mental health and preventing substance abuse and violence in elementary students: a randomized control study of the Michigan Model for Health. Journal of School Health 2011;81(6):320‐30. - PubMed
Olton 1985 {published data only}
-
- Olton AL. The effect of locus of control and perceptions of school environment on outcome in three school drug abuse prevention programs. Journal of Drug Education 1985;15(2):157‐69. - PubMed
Pentz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Dwyer JH, MacKinnon DP, Pentz MA, Flay BR, Hansen WB, Wang EYI, et al. Estimating intervention effects in longitudinal studies. American Journal of Epidemiology 1989;130(4):781‐95. - PubMed
-
- Johnson CA, Pentz MA, Weber MD, Dwyer JH, Baer N, MacKinnon DP, et al. Relative effectiveness of comprehensive community programming for drug abuse prevention with high‐risk and low‐risk adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(4):447‐56. - PubMed
-
- MacKinnon DP, Anderson Jonhson C, Pentz MA, Dwer JH, Hansen WB, Flay BD, et al. Mediating mechanisms in a school‐based drug prevention program: first ‐year effects of the Midwestern Prevention Project. Health Psychology 1991;10(3):164‐72. - PubMed
-
- Pentz MA, Dwer JH, MacKinnon DP, Flay BD, Hansen WB, Wang EYI, et al. A multi community trial for primary prevention of adolescent drug abuse. JAMA 1989;261(22):3259‐66. - PubMed
Petoskey 1998 {published data only}
-
- Petoskey EL, Stelle KR, Jong JA. Prevention through empowerment in a Native American community. Drugs Society 1998;12(1/2):147‐62.
Prinz 2000 {published data only}
-
- Prinz RJ, Dumas JE, Smith EP, Laughlin JE. The EARLY ALLIANCE prevention trial: a dual design to test reduction of risk for conduct problems, substance abuse, and school failure in childhood. Controlled Clinical Trials 2000;21:286‐302. - PubMed
Raghupathy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Raghupathy S, Forth AL. The HAWK2 program: a computer‐based drug prevention intervention for Native American youth. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2012;38(5):461‐7. - PubMed
Raynal 1996 {published data only}
-
- Raynal ME, Chen WW. Evaluation of a drug prevention program for young high risk students. International Quarterly of Community Health Education 1996;16(2):187‐95. - PubMed
Reynolds 1995 {published data only}
-
- Reynolds J, Cooper DL. A community and school approach to drug prevention and early intervention with high risk elementary school children. Journal of Primary Prevention 1995;15(4):377‐85. - PubMed
Ringwalt 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ringwalt C, Pankratz M, Gottfredson N, Jackson‐Newsom J, Dusenbury L, Giles S, et al. The effects of students' curriculum engagement, attitudes toward their teachers, and perception of their teachers' skills on school‐based prevention curriculum outcomes. Journal of Drug Education 2009;39(3):223‐37. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ringwalt C, Pankratz M, Hansen W, Dusenbury L, Jackson‐Newsom J, Giles S, et al. The potential of coaching as a strategy to improve the effectiveness of school‐based substance use prevention curricula. Health Education & Behavior 2009;36(4):696‐710. - PubMed
Ringwalt 2011 {published data only}
Rollin 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rollin SA, Rubin R, Hardy‐Blake B, Allen P, et al. Project KICK: a school‐based drug education research project: peers, parents and kids. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 1994;39(3):75‐86.
-
- Rollin SA, Rubin R, Marcil R, Ferullo U, Buncher R. Project KICK: a school‐based drug education health promotion research project. Counselling Psychology Quarterly 1995;8(4):345‐59.
Rosenbaum 1994 {published data only}
-
- Ennett ST, Rosenbaum DP, Flewelling RL, Bieler GS, Ringwalt CL, Bailey SL. Long‐term evaluation of Drug Abuse Resistance Education. Addictive Behaviors 1994;19(2):113‐25. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum DP, Flewelling RL, Bailey SL, Ringwalt CL, Wilkinson DL. Cops in the classroom: a longitudinal evaluation of drug abuse resistance education (DARE). Journal of Research Crime Delinquency 1994;31(1):3‐31.
-
- Rosenbaum DP, Hanson GS. Assessing the effects of school‐based drug education: a six‐year multilevel analysis of project DARE. Journal of Research Crime Delinquency 1998;35(4):381‐412.
Ross 1998 {published data only}
Sarvela 1987 {published data only}
-
- Sarvela PD, McClendon EJ. An impact evaluation of a rural youth drug education program. Journal of Drug Education 1987;17(3):213‐31. - PubMed
Schaps 1982 {published data only}
-
- Schaps E, Moskowitz JM, Condon JW, Malvin JH. Process and outcome evaluation of a drug education course. Journal of Drug Education 1982;12(4):353‐64. - PubMed
Schinke 1988 {published data only}
-
- Schinke SP, Bebel MY, Orlandi MA, Botvin GJ. Prevention strategies for vulnerable pupils: school social work practices to prevent substance abuse. Urban Education 1988;22(4):510‐9.
Schinke 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schinke SP, Tepavac L, Cole KC. Preventing substance use among native American youth: three‐year results. Addictive Behavior 2000;25(3):387‐97. - PubMed
Shetgiri 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shetgiri R, Kataoka S, Lin H, Flores G. A randomized, controlled trial of a school‐based intervention to reduce violence and substance use in predominantly Latino high school students. Journal of the National Medical Association 2011;103(9‐10):932‐40. - PubMed
Shope 1996 {published data only}
-
- Shope JT, Copeland LA, Kamp ME, Lang SW. Twelfth grade follow‐up of the effectiveness of a middle school‐based substance abuse prevention program. Journal of Drug Education 1998;28(3):185‐97. - PubMed
-
- Shope JT, Copeland LA, Marcoux BC, Kamp ME. Effectiveness of a school‐based substance abuse prevention program. Journal of Drug Education 1996;26(4):323‐37. - PubMed
Short 1998 {published data only}
-
- Short JL. Evaluation of a substance abuse prevention and mental health promotion program for children of divorce. Journal of Divorce & Remarriage 1998;28(3/4):139‐55.
Skroban 1999 {published data only}
-
- Skroban SB, Gottfredson DC, Gottfredson GD. School‐based social competency promotion demonstration. Evaluation Review 1999;23(1):2‐27. - PubMed
Snow 1997 {published data only}
-
- Snow DL, Tebes JK, Ayers TS. Impact of two social‐cognitive interventions to prevent adolescent substance use: test of an amenability to treatment model. Journal of Drug Education 1997;27(1):1‐17. - PubMed
Spoth 2013 {published data only}
Stevens 1996 {published data only}
-
- Stevens MM, Freeman DH, Mott L, Youells F. Three‐year results of prevention programs on marijuana use: the New Hampshire Study. Journal of Drug Education 1996;26(3):257‐73. - PubMed
Stormshak 2011 {published data only}
Sussman 2012 {published data only}
Tatchell 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tatchell TW. Substance abuse prevention in sixth grade: The effect of a prevention program on adolescents' risk and protective factors. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. University of Utah, 2001.
Teesson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Teesson M, Newton N, Slade T, Conrod P. An integrated approach to substance use prevention for high‐and low risk youth: The cap intervention. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:148A.
Tibbits 2011 {published data only}
Valentine 1998 {published data only}
-
- Valentine J, Griffith J, Ruthazer R, Gottlieb B, Keel S. Strengthening causal inference in adolescent drug prevention studies: methods and findings from a controlled study of the Urban Youth Connection Program. Drugs and Society 1998;12(1/2):127‐45.
Valentine 1998a {published data only}
-
- Valentine J, Gottlieb B, Keel S, Griffith J, Ruthazer R. Measuring the effectiveness of the Urban Youth Connection: the case for dose‐response modelling to demonstrate the impact of an adolescent substance abuse prevention program. Journal of Primary Prevention 1998;18(3):363‐87.
Villalbì 1993 {published data only}
-
- Villalbì JR, Aubà J, Gonzalez AG. Results of a school prevention programme on the substances abuse: project of a pilot study in Barcelona [Resultados de un programa escolar de prevencion del abuso de sustancias asictivas: proyecto piloto pase de Barcelona]. Gaceta Sanitaria 1993;7:70‐7. - PubMed
Weiss 1998 {published data only}
-
- Weiss FL, Nicholson HJ. Friendly PEERsuasion against substance use: the Girls Incorporated Model and Evaluation. Drugs and Society 1998;12(1‐2):7‐22.
West 2008 {published data only}
-
- West B, Abatemarco D, Ohman‐Strickland P, Zec V, Russo A, Milic R. Project Northland in Croatia: results and lesson learned. Journal of Drug Education 2008;38(1):56‐70. - PubMed
Wherch 2005 b {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Moore MM, DiClemente CC, Owen DM, Carlson JM, Jobli E. Single vs multiple prevention: is more always better? A pilot study. Substance Use and Misuse 2005;40:1085‐101. - PubMed
Young 1997 {published data only}
-
- Young M, Kelley RM, Denny G. Evaluation of selected life‐skill modules from the contemporary health series with students in grade 6. Perceptual and Motor Skills 1997;84:811‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Gubanich 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gubanich PJ, Kimmerle KM, Gubanich KM, Gottschalk AW, Miniaci A. Interim analysis of a 2‐year childhood wellness intervention: a gain in knowledge. Clinical Journal of Sports Medicine 2011;21(2):155‐6.
Poduska 2009 {published data only}
-
- Poduska J, Kellam S, Brown CH, Ford C, Windham A, Keegan N, et al. Study protocol for a group randomized controlled trial of a classroom‐based intervention aimed at preventing early risk factors for drug abuse: integrating effectiveness and implementation research. Implement Science 2009;4:56. - PMC - PubMed
Seal 2006 {published data only}
-
- Seal N. Preventing tobacco and drug use among Thai high school students through life skills training. Nursing and Health Sciences 2006;8:164‐8. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Bannink 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bannink R, Joosten‐van Zwanenburg E, Looij‐Jansen P, As E, Raat H. Evaluation of computer‐tailored health education ('E‐health4Uth') combined with personal counselling ('E‐health4Uth + counselling') on adolescents' behaviours and mental health status: design of a three‐armed cluster randomised controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2012;12:1083. - PMC - PubMed
Hodder 2012 {published data only}
Midford 2012 {published data only}
Newton 2012a {published data only}
-
- Newton NC, Teesson M, Conrod P, Slade T, Barrett EL. Developing the cap intervention: A comprehensive model for alcohol and drug prevention. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:350A.
Additional references
AIHW 2011
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. 2010 National Drug Strategy Household Survey report. Drug Statistics Series no. 25. Cat. no. PHE 145. Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2011.
Ajzen 1985
-
- Ajzen I. From decisions to actions: a theory of planned behavior. In: Kuhl J, Beckmann J editor(s). Action‐control: From Cognition to Behavior. New York: Springer, 1985:11‐39.
Altobelli 2005
-
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Tiberti S, Petrocelli R, Cicioni L, Orio F, et al. Association between drug, alcohol and tobacco use in adolescents and social‐familiar factors [Associazione tra l'uso di sostanze stupefacenti, alcol e tabacco negli adolescenti e contesto socio‐familiare]. Annali d'Igiene 2005;17:57‐65. - PubMed
Amato 2007
-
- Amato L, Davoli M, Ali R, Faggiano F, Farrell M, Foxcroft D, et al. Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group. About The Cochrane Collaboration (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2007, Issue 10. Art. No.: ADDICTN. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Bandura 1977
-
- Bandura A. Social Learning Theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1977.
Bangert‐Drowns 1988
-
- Bangert‐Drowns RL. The effects of school‐based substance abuse education. Journal of Drug Education 1988;18:243‐64. - PubMed
Cuijpers 2002a
-
- Cuijpers P. Effective ingredients of school‐based drug prevention programs. A systematic review. Addictive Disorders 2002;27:1009‐23. - PubMed
Dortmizer 2004
-
- Dortmizer CM, Gonzalez GB, Penna M, Bejarano J, Obando P, Sanchez M, et al. The PACARDO research project: youthful drug involvement in Central America and the Dominican Republic. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública 2004;15(6):400‐16. - PubMed
DSM‐5
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5). Fifth. American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
EMCDDA 2012
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Annual Report: The state of the drugs problem in Europe. 2012. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA).
Ennett 1994
ESPAD 2011
-
- Hibell B, Guttormsson U, Ahlström S, Balakireva O, Bjarnason T, Kokkevi A, et al. ESPAD report 2011. http://www.espad.org/Uploads/ESPAD_reports/2011/The_2011_ESPAD_Report_FU... 2011.
Evans 1976
-
- Evans RI. Smoking in children: Developing a social psychological strategy of deterrence. Preventive Medicine 1976;5:122‐7. - PubMed
Faggiano 2005
Fergusson 2000
-
- Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ. Does cannabis use encourage other forms of illicit drug use?. Addiction 2000;95:505‐20. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2011
Glass 1981
-
- Glass G, McGaw B, Smith M. Meta‐analysis in Social Research. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications, 1981.
Green 1991
-
- Green LW, Kreuter MW. Health promotion today and a framework for planning. In: Green LW, Kreuter MW editor(s). Health Promotion Planning: an Educational and Environmental Approach. 2nd Edition. Mountain View, CA: Mayfield Pub Co, 1991:1‐43.
Griffin 2010
Hansen 1992
-
- Hansen WB. School‐based substance abuse prevention: a review of the state of the art in curriculum, 1980‐1990. Health Education Research 1992;7:403‐30. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Johnston 2013
-
- Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future. National Survey Results on Drug Use: 2012 Overview. Key Findings on Adolescent Drug Use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan, 2013.
Kandel 1975
-
- Kandel D. Stages in adolescent involvement in drug use. Science 1975;190:912‐4. - PubMed
Kroger 1994
-
- Kroger CB. A review of the effectiveness of health education and health promotion. International Union for Health Promotion and Education. Vol. 8, Utrecht: IUPHE, 1994:1‐73.
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J on behalf of the Cochrane Information Retrieval Methods Group. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Leshner 1997
-
- Leshner AI. Drug abuse and addiction treatment research: the next generation. Archives of General Psychiatry 1997;54:691‐4. - PubMed
Leshner 1999
-
- Leshner AI. Science‐based views of drug addiction and its treatment. JAMA 1999;282:1314‐6. - PubMed
MacMahon 2001
-
- MacMahon S, Collins R. Reliable assessment of the effects of treatment on mortality and major morbidity, II: observational studies. Lancet 2001;357:455‐61. - PubMed
McBride 2003
-
- McBride N. A systematic review of school drug education. Health Education Research 2003;18:729‐42. - PubMed
McGuire 1968
-
- McGuire WJ. The nature of attitudes and attitude change. In: Lindzey G, Aronson E editor(s). Handbook of Social Psychology. Reading, MA: Addison‐Wesley, 1968:136–314.
Mellanby 2000
-
- Mellanby AR, Rees JB, Tripp JH. Peer‐led and adult‐led school health education: a critical review of available comparative research. Health Education Research 2000;15:533‐45. - PubMed
Midford 2010
-
- Midford M. Drug prevention programmes for young people: where have we been and where should we be going?. Addiction 2010;105:1688‐95. - PubMed
Morral 2002
-
- Morral AR, McCaffrey DF, Paddock SM. Reassessing the marijuana gateway effect. Addiction 2002;97:1493‐504. - PubMed
Porath‐Waller 2010
-
- Porath‐Waller AJ, Beasley E, Beirness DJ. Meta‐analytic review of school‐based prevention for cannabis use. Health Education & Behavior 2010;37:709‐23. - PubMed
SAMHSA 2012
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2012 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings. NSDUH Series H‐46, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 13‐4795. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2012.
Skara 2003
-
- Skara S, Sussman S. A review of 25 long‐term adolescent tobacco and other drug use prevention program evaluations. Preventive Medicine 2003;37:451‐74. - PubMed
Sterne 2001
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Davey Smith G. Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care. BMJ Publishing Group, 2001.
Thomas 2006
Thomas 2013
Tobler 1986
-
- Tobler NS. Meta‐analysis of 143 adolescent drug prevention programs: quantitative outcome results of a program participants compared to a control or comparison group. Journal of Drug Issues 1986;16(4):537‐67.
Tobler 1997
-
- Tobler NS, Stratton HH. Effectiveness of school‐based drug prevention programs: a meta‐analysis of the research. Journal of Primary Prevention. 1997;18(1):71‐128.
Tobler 2000
-
- Tobler NS, Roona MR, Ochshorn PM, Diana G, Streke AV, Stackpole KM. School‐based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta‐analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention 2000;20(4):275‐336.
White 1997
-
- White D, Pitts M. Health Promotion with Young People for the Prevention of Substance Misuse. London: Health Education Authority, 1997.
White 1998
-
- White D, Pitts M. Educating young people about drugs: a systematic review. Addiction 1998;93:1475‐87. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

