Population testing for cancer predisposing BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations in the Ashkenazi-Jewish community: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25435541
- PMCID: PMC4301703
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/dju379
Population testing for cancer predisposing BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations in the Ashkenazi-Jewish community: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Technological advances raise the possibility of systematic population-based genetic testing for cancer-predisposing mutations, but it is uncertain whether benefits outweigh disadvantages. We directly compared the psychological/quality-of-life consequences of such an approach to family history (FH)-based testing.
Methods: In a randomized controlled trial of BRCA1/2 gene-mutation testing in the Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) population, we compared testing all participants in the population screening (PS) arm with testing those fulfilling standard FH-based clinical criteria (FH arm). Following a targeted community campaign, AJ participants older than 18 years were recruited by self-referral after pretest genetic counseling. The effects of BRCA1/2 genetic testing on acceptability, psychological impact, and quality-of-life measures were assessed by random effects regression analysis. All statistical tests were two-sided.
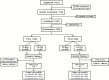
Results: One thousand, one hundred sixty-eight AJ individuals were counseled, 1042 consented, 1034 were randomly assigned (691 women, 343 men), and 1017 were eligible for analysis. Mean age was 54.3 (SD = 14.66) years. Thirteen BRCA1/2 carriers were identified in the PS arm, nine in the FH arm. Five more carriers were detected among FH-negative FH-arm participants following study completion. There were no statistically significant differences between the FH and PS arms at seven days or three months on measures of anxiety, depression, health anxiety, distress, uncertainty, and quality-of-life. Contrast tests indicated that overall anxiety (P = .0001) and uncertainty (P = .005) associated with genetic testing decreased; positive experience scores increased (P = .0001); quality-of-life and health anxiety did not change with time. Overall, 56% of carriers did not fulfill clinical criteria for genetic testing, and the BRCA1/2 prevalence was 2.45%.
Conclusion: Compared with FH-based testing, population-based genetic testing in Ashkenazi Jews doesn't adversely affect short-term psychological/quality-of-life outcomes and may detect 56% additional BRCA carriers.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, et al. The risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(20):1401–1408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous