Cost-effectiveness of population screening for BRCA mutations in Ashkenazi jewish women compared with family history-based testing
- PMID: 25435542
- PMCID: PMC4301704
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/dju380
Cost-effectiveness of population screening for BRCA mutations in Ashkenazi jewish women compared with family history-based testing
Abstract
Background: Population-based testing for BRCA1/2 mutations detects the high proportion of carriers not identified by cancer family history (FH)-based testing. We compared the cost-effectiveness of population-based BRCA testing with the standard FH-based approach in Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) women.
Methods: A decision-analytic model was developed to compare lifetime costs and effects amongst AJ women in the UK of BRCA founder-mutation testing amongst: 1) all women in the population age 30 years or older and 2) just those with a strong FH (≥10% mutation risk). The model assumes that BRCA carriers are offered risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy and annual MRI/mammography screening or risk-reducing mastectomy. Model probabilities utilize the Genetic Cancer Prediction through Population Screening trial/published literature to estimate total costs, effects in terms of quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), cancer incidence, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), and population impact. Costs are reported at 2010 prices. Costs/outcomes were discounted at 3.5%. We used deterministic/probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) to evaluate model uncertainty.
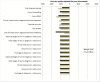
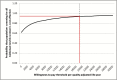
Results: Compared with FH-based testing, population-screening saved 0.090 more life-years and 0.101 more QALYs resulting in 33 days' gain in life expectancy. Population screening was found to be cost saving with a baseline-discounted ICER of -£2079/QALY. Population-based screening lowered ovarian and breast cancer incidence by 0.34% and 0.62%. Assuming 71% testing uptake, this leads to 276 fewer ovarian and 508 fewer breast cancer cases. Overall, reduction in treatment costs led to a discounted cost savings of £3.7 million. Deterministic sensitivity analysis and 94% of simulations on PSA (threshold £20000) indicated that population screening is cost-effective, compared with current NHS policy.
Conclusion: Population-based screening for BRCA mutations is highly cost-effective compared with an FH-based approach in AJ women age 30 years and older.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Levy-Lahad E, Gabai-Kapara E, Kaufman B, et al. Identification of BRCA1/BRCA2 carriers by screening in the healthy population and its implications. In: American Society of Clinical Oncology, Annual meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(Suppl);abstr 1513.
-
- Metcalfe KA, Poll A, Royer R, et al. Screening for founder mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 in unselected Jewish women. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(3):387–391. - PubMed
-
- King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB. Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science. 2003;302(5645):643–646. - PubMed
-
- Hopper JL, Southey MC, Dite GS, et al. Population-based estimate of the average age-specific cumulative risk of breast cancer for a defined set of protein-truncating mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Australian Breast Cancer Family Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999;8(9):741–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

