The cultivation of Bt corn producing Cry1Ac toxins does not adversely affect non-target arthropods
- PMID: 25437213
- PMCID: PMC4250226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114228
The cultivation of Bt corn producing Cry1Ac toxins does not adversely affect non-target arthropods
Abstract
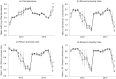
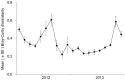
Transgenic corn producing Cry1Ac toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) provides effective control of Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée), and thus reduces insecticide applications. However, whether Bt corn exerts undesirable effects on non-target arthropods (NTAs) is still controversial. We conducted a 2-yr study in Shangzhuang Agricultural Experiment Station to assess the potential impact of Bt corn on field population density, biodiversity, community composition and structure of NTAs. On each sampling date, the total abundance, Shannon's diversity index, Pielou's evenness index and Simpson's diversity index were not significantly affected by Bt corn as compared to non-Bt corn. The "sampling dates" had a significant effect on these indices, but no clear tendencies related to "Bt corn" or "sampling dates X corn variety" interaction were recorded. Principal response curve analysis of variance indicated that Bt corn did not alter the distribution of NTAs communities. Bray-Curtis dissimilarity and distance analysis showed that Cry1Ac toxin exposure did not increase community dissimilarities between Bt and non-Bt corn plots and that the evolution of non-target arthropod community was similar on the two corn varieties. The cultivation of Bt corn failed to show any detrimental evidence on the density of non-target herbivores, predators and parasitoids. The composition of herbivores, predators and parasitoids was identical in Bt and non-Bt corn plots. Taken together, results from the present work support that Bt corn producing Cry1Ac toxins does not adversely affect NTAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- James C, Krattiger AF (1996) Global review of the field testing and commercialization of transgenic plants, 1986 to 1995: the first decade of crop biotechnology. ISAAA Brief No. 1. ISAAA, Ithaca, NY.
-
- James C (2013) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2013. ISAAA Brief No. 46. ISAAA, Ithaca, NY.
-
- Romeis J, Meissle M, Bigler F (2006) Transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins and biological control. Nat Biotechnol 24:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Desneux N, Bernal JS (2010) Genetically modified crops deserve greater ecotoxicological scrutiny. Ecotoxicology 19:1642–1644. - PubMed
-
- Wu KM, Lu YH, Feng HQ, Jiang YY, Zhao JZ (2008) Suppression of cotton bollworm in multiple crops in China in areas with Bt toxin-containing cotton. Science 321:1676–1678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

