Gout: a review of nonmodifiable and modifiable risk factors
- PMID: 25437279
- PMCID: PMC4251556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.07.002
Gout: a review of nonmodifiable and modifiable risk factors
Abstract
Gout is a common inflammatory arthritis triggered by the crystallization of uric acid within the joints. Gout affects millions worldwide and has an increasing prevalence. Recent research has been carried out to better qualify and quantify the risk factors predisposing individuals to gout. These can largely be broken into nonmodifiable risk factors, such as gender, age, race, and genetics, and modifiable risk factors, such as diet and lifestyle. Increasing knowledge of factors predisposing certain individuals to gout could potentially lead to improved preventive practices. This review summarizes the nonmodifiable and modifiable risk factors associated with development of gout.
Keywords: Diet; Genetics; Gout; Race; Risk factors; Sex.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

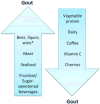
References
-
- Lipkowitz MS. Regulation of uric acid excretion by the kidney. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14(2):179–88. - PubMed
-
- Campion EW, Glynn RJ, DeLabry LO. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Risks and consequences in the Normative Aging Study. Am J Med. 1987;82(3):421–6. - PubMed
-
- Bhole V, de Vera M, Rahman MM, Krishnan E, Choi H. Epidemiology of gout in women: Fifty-two-year followup of a prospective cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(4):1069–76. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):3136–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

