Fine-scale chromatin interaction maps reveal the cis-regulatory landscape of human lincRNA genes
- PMID: 25437436
- PMCID: PMC4281301
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3205
Fine-scale chromatin interaction maps reveal the cis-regulatory landscape of human lincRNA genes
Abstract
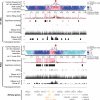
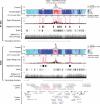
High-throughput methods based on chromosome conformation capture have greatly advanced our understanding of the three-dimensional (3D) organization of genomes but are limited in resolution by their reliance on restriction enzymes. Here we describe a method called DNase Hi-C for comprehensively mapping global chromatin contacts. DNase Hi-C uses DNase I for chromatin fragmentation, leading to greatly improved efficiency and resolution over that of Hi-C. Coupling this method with DNA-capture technology provides a high-throughput approach for targeted mapping of fine-scale chromatin architecture. We applied targeted DNase Hi-C to characterize the 3D organization of 998 large intergenic noncoding RNA (lincRNA) promoters in two human cell lines. Our results revealed that expression of lincRNAs is tightly controlled by complex mechanisms involving both super-enhancers and the Polycomb repressive complex. Our results provide the first glimpse of the cell type-specific 3D organization of lincRNA genes.
Figures
















References
-
- Guelen L, et al. Domain organization of human chromosomes revealed by mapping of nuclear lamina interactions. Nature. 453:948–951. - PubMed
-
- Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 2002;295:1306–1311. - PubMed
-
- Simonis M, et al. Nuclear organization of active and inactive chromatin domains uncovered by chromosome conformation capture-on-chip (4C). Nature genetics. 2006;38:1348–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

