Mending a broken heart: the role of mitophagy in cardioprotection
- PMID: 25437922
- PMCID: PMC4312945
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00708.2014
Mending a broken heart: the role of mitophagy in cardioprotection
Abstract
The heart is highly energy dependent with most of its energy provided by mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria also play a role in many other essential cellular processes including metabolite synthesis and calcium storage. Therefore, maintaining a functional population of mitochondria is critical for cardiac function. Efficient degradation and replacement of dysfunctional mitochondria ensures cell survival, particularly in terminally differentiated cells such as cardiac myocytes. Mitochondria are eliminated via mitochondrial autophagy or mitophagy. In the heart, mitophagy is an essential housekeeping process and required for cardiac homeostasis. Reduced autophagy and accumulation of impaired mitochondria have been linked to progression of heart failure and aging. In this review, we discuss the pathways that regulate mitophagy in cells and highlight the cardioprotective role of mitophagy in response to stress and aging. We also discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting mitophagy and directions for future investigation.
Keywords: BNIP3; FUNDC1; autophagy; mitochondria; mitophagy; parkin.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

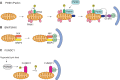
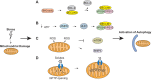

References
-
- Baines CP. The cardiac mitochondrion: nexus of stress. Annu Rev Physiol 72: 61–80, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Bingol B, Tea JS, Phu L, Reichelt M, Bakalarski CE, Song Q, Foreman O, Kirkpatrick DS, Sheng M. The mitochondrial deubiquitinase USP30 opposes parkin-mediated mitophagy. Nature 510: 370–375, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG-23039/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-67724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-91469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-112330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-101217/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL-007444/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007444/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-085577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-087023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023039/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

