Magnetic particle imaging with tailored iron oxide nanoparticle tracers
- PMID: 25438306
- PMCID: PMC4428902
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2375065
Magnetic particle imaging with tailored iron oxide nanoparticle tracers
Abstract
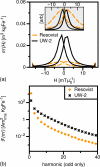
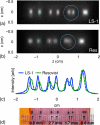
Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) shows promise for medical imaging, particularly in angiography of patients with chronic kidney disease. As the first biomedical imaging technique that truly depends on nanoscale materials properties, MPI requires highly optimized magnetic nanoparticle tracers to generate quality images. Until now, researchers have relied on tracers optimized for MRI T2(∗) -weighted imaging that are sub-optimal for MPI. Here, we describe new tracers tailored to MPI's unique physics, synthesized using an organic-phase process and functionalized to ensure biocompatibility and adequate in vivo circulation time. Tailored tracers showed up to 3 × greater signal-to-noise ratio and better spatial resolution than existing commercial tracers in MPI images of phantoms.
Figures
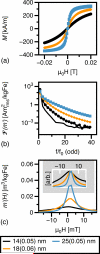
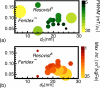
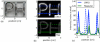
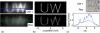
References
-
- Gleich B, Weizenecker J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature. 2005 Jul;435(7046):1214–1217. - PubMed
-
- Goodwill PW, Saritas EU, Croft LR, Kim TN, Krishnan KM, Schaffer DV, Conolly SM. X-Space MPI: Magnetic Nanoparticles for Safe Medical Imaging. Advanced Materials. 2012;24:3870–3877. - PubMed
-
- Weizenecker J, Gleich B, Rahmer J, Dahnke H, Borgert J. Three-dimensional real-time in vivo magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009;54(5):L1–L10. - PubMed
-
- Weizenecker J, Borgert J, Gleich B. A simulation study on the resolution and sensitivity of magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007;52:6363–6374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

