Truncating and missense mutations in IGHMBP2 cause Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 2
- PMID: 25439726
- PMCID: PMC4225647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.10.002
Truncating and missense mutations in IGHMBP2 cause Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 2
Abstract
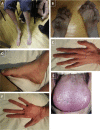
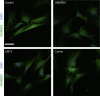
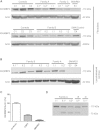
Using a combination of exome sequencing and linkage analysis, we investigated an English family with two affected siblings in their 40s with recessive Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 2 (CMT2). Compound heterozygous mutations in the immunoglobulin-helicase-μ-binding protein 2 (IGHMBP2) gene were identified. Further sequencing revealed a total of 11 CMT2 families with recessively inherited IGHMBP2 gene mutations. IGHMBP2 mutations usually lead to spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1 (SMARD1), where most infants die before 1 year of age. The individuals with CMT2 described here, have slowly progressive weakness, wasting and sensory loss, with an axonal neuropathy typical of CMT2, but no significant respiratory compromise. Segregating IGHMBP2 mutations in CMT2 were mainly loss-of-function nonsense in the 5' region of the gene in combination with a truncating frameshift, missense, or homozygous frameshift mutations in the last exon. Mutations in CMT2 were predicted to be less aggressive as compared to those in SMARD1, and fibroblast and lymphoblast studies indicate that the IGHMBP2 protein levels are significantly higher in CMT2 than SMARD1, but lower than controls, suggesting that the clinical phenotype differences are related to the IGHMBP2 protein levels.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Skre H. Genetic and clinical aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth’s disease. Clin. Genet. 1974;6:98–118. - PubMed
-
- Harel T., Lupski J.R. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and pathways to molecular based therapies. Clin Genet. 2014 Published online May 9, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Reilly M.M., Shy M.E. Diagnosis and new treatments in genetic neuropathies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2009;80:1304–1314. - PubMed
-
- Shy M.E. Inherited peripheral neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2011;17:294–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G108/638/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 309548/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- 096919/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0802760/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K000608/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/J004758/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

