Specialized metabolites from the microbiome in health and disease
- PMID: 25440054
- PMCID: PMC4337795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.10.016
Specialized metabolites from the microbiome in health and disease
Abstract
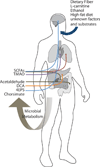
The microbiota, and the genes that comprise its microbiome, play key roles in human health. Host-microbe interactions affect immunity, metabolism, development, and behavior, and dysbiosis of gut bacteria contributes to disease. Despite advances in correlating changes in the microbiota with various conditions, specific mechanisms of host-microbiota signaling remain largely elusive. We discuss the synthesis of microbial metabolites, their absorption, and potential physiological effects on the host. We propose that the effects of specialized metabolites may explain present knowledge gaps in linking the gut microbiota to biological host mechanisms during initial colonization, and in health and disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Amann A, Costello B, de L, Miekisch W, Schubert J, Buszewski B, Pleil J, Ratcliffe N, Risby T. The human volatilome: volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath, skin emanations, urine, feces and saliva. J. Breath Res. 2014;8:034001. - PubMed
-
- Belcheva A, Irrazabal T, Robertson SJ, Streutker C, Maughan H, Rubino S, Moriyama EH, Copeland JK, Kumar S, Green B, et al. Gut Microbial Metabolism Drives Transformation of Msh2-Deficient Colon Epithelial Cells. Cell. 2014;158:288–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH100556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM099535/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH100556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI095125/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM095384/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095384/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM099535/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS085910/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095125/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK078938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

