Computer-automated time-lapse analysis results correlate with embryo implantation and clinical pregnancy: a blinded, multi-centre study
- PMID: 25444507
- PMCID: PMC4575500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.09.005
Computer-automated time-lapse analysis results correlate with embryo implantation and clinical pregnancy: a blinded, multi-centre study
Abstract
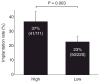
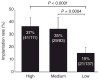
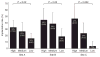
Computer-automated time-lapse analysis has been shown to improve embryo selection by providing quantitative and objective information to supplement traditional morphology. In this multi-centre study, the relationship between such computer-derived outputs (High, Medium, Low scores), embryo implantation and clinical pregnancy were examined. Data were collected from six clinics, including 205 patients whose embryos were imaged by the Eeva(TM) System. The Eeva scores were blinded and not considered during embryo selection. Embryos with High and Medium scores had significantly higher implantation rates than those with Low scores (37% and 35% versus 15%; P < 0.0001; P = 0.0004). Similar trends in implantation rates were observed in different IVF centres each using their own protocols. Further analysis revealed that patients with at least one High embryo transferred had significantly higher clinical pregnancy rates than those with only Low embryos transferred (51% versus 34%; P = 0.02), although patients' clinical characteristics across groups were comparable. These data, together with previous research and clinical studies, confirm that computer-automated Eeva scores provide valuable information, which may improve the clinical outcome of IVF procedures and ultimately facilitate the trend of single embryo selection.
Keywords: Eeva Test; embryo selection; implantation; in-vitro fertilization; pregnancy; time-lapse.
Copyright © 2014 Reproductive Healthcare Ltd. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abeyta M, Behr B. Morphological assessment of embryo viability. Semin Reprod Med. 2014;32:114–126. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar J, Motato Y, Escriba MJ, Ojeda M, Munoz E, Meseguer M. The human first cell cycle: impact on implantation. Reprod Biomed Online. 2014;28:475–484. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio B, Cruz M, Meseguer M. Is morphokinetic analysis the answer? Reprod Biomed Online. 2013;27:654–663. - PubMed
-
- Athayde Wirka K, Chen AA, Conaghan J, Ivani K, Gvakharia M, Behr B, Suraj V, Tan L, Shen S. Atypical embryo phenotypes identified by time-lapse microscopy: high prevalence and association with embryo development. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:1637–1648. e5. - PubMed
-
- Basile N, Morbeck D, Garcia-Velasco J, Bronet F, Meseguer M. Type of culture media does not affect embryo kinetics: a time-lapse analysis of sibling oocytes. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:634–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

