Brivaracetam differentially affects voltage-gated sodium currents without impairing sustained repetitive firing in neurons
- PMID: 25444522
- PMCID: PMC4359682
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12347
Brivaracetam differentially affects voltage-gated sodium currents without impairing sustained repetitive firing in neurons
Abstract
Aims: Brivaracetam (BRV) is an antiepileptic drug in Phase III clinical development. BRV binds to synaptic vesicle 2A (SV2A) protein and is also suggested to inhibit voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs). To evaluate whether the effect of BRV on VGSCs represents a relevant mechanism participating in its antiepileptic properties, we explored the pharmacology of BRV on VGSCs in different cell systems and tested its efficacy at reducing the sustained repetitive firing (SRF).
Methods: Brivaracetam investigations on the voltage-gated sodium current (I(Na)) were performed in N1E-155 neuroblastoma cells, cultured rat cortical neurons, and adult mouse CA1 neurons. SRF was measured in cultured cortical neurons and in CA1 neurons. All BRV (100-300 μM) experiments were performed in comparison with 100 μM carbamazepine (CBZ).
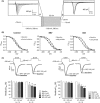
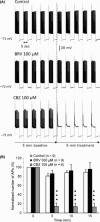
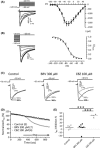
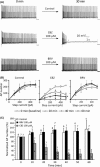
Results: Brivaracetam and CBZ reduced IN a in N1E-115 cells (30% and 40%, respectively) and primary cortical neurons (21% and 47%, respectively) by modulating the fast-inactivated state of VGSCs. BRV, in contrast to CBZ, did not affect I(Na) in CA1 neurons and SRF in cortical and CA1 neurons. CBZ consistently inhibited neuronal SRF by 75-93%.
Conclusions: The lack of effect of BRV on SRF in neurons suggests that the reported inhibition of BRV on VGSC currents does not contribute to its antiepileptic properties.
Keywords: Action potential firing; Antiepileptic drug; Neurons; Voltage-gated sodium channel.
© 2014 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employed by UCB Pharma, Belgium.
Figures

References
-
- Kasteleijn‐Nolst Trenite DG, Genton P, Parain D, et al. Evaluation of brivaracetam, a novel SV2A ligand, in the photosensitivity model. Neurology 2007;69:1027–1034. - PubMed
-
- Malawska B, Kulig K. Brivaracetam: A new drug in development for epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2008;17:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Van Paesschen W, Hirsch E, Johnson M, Falter U, von Rosenstiel P. Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with uncontrolled partial‐onset seizures: A phase IIb, randomized, controlled trial. Epilepsia 2013;54:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Kwan P, Trinka E, Van Paesschen W, Rektor I, Johnson ME, Lu S. Adjunctive brivaracetam for uncontrolled focal and generalized epilepsies: Results of a phase III, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled, flexible‐dose trial. Epilepsia 2014;55:38–46. - PubMed
-
- Ryvlin P, Werhahn KJ, Blaszczyk B, Johnson ME, Lu S. Adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with uncontrolled focal epilepsy: Results from a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Epilepsia 2014;55:47–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

