Arsenic trioxide amplifies cisplatin toxicity in human tubular cells transformed by HPV-16 E6/E7 for further therapeutic directions in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25444910
- PMCID: PMC4259818
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.008
Arsenic trioxide amplifies cisplatin toxicity in human tubular cells transformed by HPV-16 E6/E7 for further therapeutic directions in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
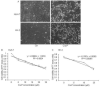
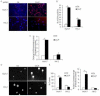
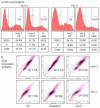
Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA integrations may affect therapeutic responses in cancers through ATM network-related DNA damage response (DDR). We studied whether cisplatin-induced DDR was altered in human HK-2 renal tubular cells immortalized by HPV16 E6/E7 genes. Cytotoxicity assays utilized thiazolyl blue dye and DDR was identified by gene expression differences, double-strand DNA breaks, ATM promoter activity, and analysis of cell cycling and side population cells. After cisplatin, HK-2 cells showed greater ATM promoter activity indicating activation of this network, but DDR was muted, since little γH2AX was expressed, DNA strand breaks were absent and cells continued cycling. When HK-2 cells were treated with the MDM2 antagonist inducing p53, nutlin-3, or p53 transcriptional activator, tenovin-1, cell growth decreased but cisplatin toxicity was unaffected. By contrast, arsenic trioxide, which by inhibiting wild-type p53-induced phosphatase-1 that serves responses downstream of p53, and by depolymerizing tubulin, synergistically enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity including loss of SP cells. Our findings demonstrated that HPV16 E6/E7 altered DDR through p53-mediated cell growth controls, which may be overcome by targeting of WIP1 and other processes, and thus should be relevant for treating renal cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated; Chemotherapy; DNA damage response; Nephrotoxicity; Renal cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins interact with the nuclear p53-binding protein 1 in an in vitro reconstructed 3D epithelium: new insights for the virus-induced DNA damage response.Virol J. 2018 Nov 16;15(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1086-4. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30445982 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide inhibits cell proliferation and human papillomavirus oncogene expression in cervical cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Sep 5;451(4):556-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.014. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25117446
-
Molecular genetic characterization of p53 mutated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells transformed with human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes.Int J Oncol. 2013 Aug;43(2):383-93. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1953. Epub 2013 May 24. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23708675 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic alterations in DNA repair genes and treatment outcome of chemoradiotherapy in cervical cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Feb;194:104240. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104240. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38122918 Review.
-
Manipulation of Epithelial Differentiation by HPV Oncoproteins.Viruses. 2019 Apr 22;11(4):369. doi: 10.3390/v11040369. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31013597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the carcinogenic potential of human papillomavirus (HPV) in urological cancers.Virol J. 2025 Feb 28;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02682-1. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40022189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-125a-5p regulates the radiosensitivity of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via HK2 targeting through the DDR pathway.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 19;14:1438722. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1438722. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39224810 Free PMC article.
-
USP19 Stabilizes TAK1 to Regulate High Glucose/Free Fatty Acid-induced Dysfunction in HK-2 Cells.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Aug;44(4):707-717. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2906-y. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38967891
-
Analysis of Molecular Mechanism of YiqiChutan Formula Regulating DLL4-Notch Signaling to Inhibit Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 12;2021:8875503. doi: 10.1155/2021/8875503. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9894642. doi: 10.1155/2024/9894642. PMID: 33628824 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
miR-155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 22;7(1):12155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06061-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28939896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattei J, da Silva RD, Sehrt D, Molina WR, Kim FJ. Targeted therapy in metastatic renal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;343:156–60. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Nie Y, Li X, Wu G, Huang Q, Cao J, Du Y, Li J, Deng R, Huang D, Chen B, Li S, Wei B. Pathol Oncol Res. Feb 16, 2014. MicroRNA-181a functions as an oncomir in gastric cancer by targeting the tumour suppressor gene ATM. Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

