Global characteristics of childhood acute promyelocytic leukemia
- PMID: 25445717
- PMCID: PMC4379131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.blre.2014.09.013
Global characteristics of childhood acute promyelocytic leukemia
Abstract
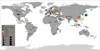
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) comprises approximately 5-10% of childhood acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases in the US. While variation in this percentage among other populations was noted previously, global patterns of childhood APL have not been thoroughly characterized. In this comprehensive review of childhood APL, we examined its geographic pattern and the potential contribution of environmental factors to observed variation. In 142 studies (spanning >60 countries) identified, variation was apparent-de novo APL represented from 2% (Switzerland) to >50% (Nicaragua) of childhood AML in different geographic regions. Because a limited number of previous studies addressed specific environmental exposures that potentially underlie childhood APL development, we gathered 28 childhood cases of therapy-related APL, which exemplified associations between prior exposures to chemotherapeutic drugs/radiation and APL diagnosis. Future population-based studies examining childhood APL patterns and the potential association with specific environmental exposures and other risk factors are needed.
Keywords: AML-M3; Acute promyelocytic leukemia; Environmental exposure; Pediatric leukemia; Risk factors; Therapy-related leukemia.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Smith has received consulting and expert testimony fees from lawyers representing both plaintiffs and defendants in cases involving claims related to exposure to chemicals and leukemia. The remaining authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kaatsch P. Epidemiology of childhood cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews. 2010;36:277–285. - PubMed
-
- Monge P, Wesseling C, Rodríguez AC, Cantor KP, Weiderpass E, Reutfors J, et al. Childhood leukaemia in Costa Rica, 1981–96. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology. 2002;16:210–218. - PubMed
-
- Deschler B, Lubbert M. Acute myeloid leukemia: epidemiology and etiology. Cancer. 2006;107:2099–2107. - PubMed
-
- Margolin JF. Molecular diagnosis and risk-adjusted therapy in pediatric hematologic malignancies: a primer for pediatricians. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:419–425. - PubMed
-
- Quintana J, Advis P, Becker A, Beresi V, Campbell M, Vines EF, et al. Acute myelogenous leukemia in Chile PINDA protocols 87 and 92 results. Leukemia. 2005;19:2143–2146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

