HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis by suppressing the JAK2-STAT3-Mcl-1 signal transduction pathway in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 25446253
- PMCID: PMC4276460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.11.013
HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis by suppressing the JAK2-STAT3-Mcl-1 signal transduction pathway in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
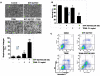
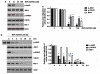
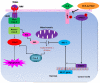
TRAIL has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, but in some cases, certain cancer cells are resistant to this ligand. In this study, we explored the ability of representative HSP90 (heat shock protein 90) inhibitor NVP-AUY922 to overcome TRAIL resistance by increasing apoptosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. The combination of TRAIL and NVP-AUY922 induced synergistic cytotoxicity and apoptosis, which was mediated through an increase in caspase activation. The treatment of NVP-AUY922 dephosphorylated JAK2 and STAT3 and decreased Mcl-1, which resulted in facilitating cytochrome c release. NVP-AUY922-mediated inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling and down-regulation of their target gene, Mcl-1, occurred in a dose and time-dependent manner. Knock down of Mcl-1, STAT3 inhibitor or JAK2 inhibitor synergistically enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Taken together, our results suggest the involvement of the JAK2-STAT3-Mcl-1 signal transduction pathway in response to NVP-AUY922 treatment, which may play a key role in NVP-AUY922-mediated sensitization to TRAIL. By contrast, the effect of the combination treatments in non-transformed colon cells was minimal. We provide a clinical rationale that combining HSP90 inhibitor with TRAIL enhances therapeutic efficacy without increasing normal tissue toxicity in CRC patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90); NVP-AUY922; Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Targeting of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways by Hsp90 inhibitor alone or in combination with berberine for treatment of colorectal cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2261-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25982393
-
The HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922-AG inhibits the PI3K and IKK signalling pathways and synergizes with cytarabine in acute myeloid leukaemia cells.Br J Haematol. 2013 Apr;161(1):57-67. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12215. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23356405
-
BAG3-dependent expression of Mcl-1 confers resistance of mutant KRAS colon cancer cells to the HSP90 inhibitor AUY922.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Feb;57(2):284-294. doi: 10.1002/mc.22755. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29068469
-
A systems biology approach to overcome TRAIL resistance in cancer treatment.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;128:142-154. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28286052 Review.
-
PRAME/EZH2-mediated regulation of TRAIL: a new target for cancer therapy.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Feb;13(2):296-304. doi: 10.2174/156652413804810727. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23228130 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring WNT pathway dysregulation in serrated colorectal cancer for improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.Front Genet. 2025 Apr 28;16:1586867. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1586867. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40357363 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cell death signalling in cancer: minimising 'Collateral damage'.Br J Cancer. 2016 Jun 28;115(1):5-11. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.111. Epub 2016 May 3. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27140313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IMPDH1, a prognostic biomarker and immunotherapy target that correlates with tumor immune microenvironment in pan-cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 22;13:983490. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.983490. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618420 Free PMC article.
-
AutoEdge-CCP: A novel approach for predicting cancer-associated circRNAs and drugs based on automated edge embedding.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Jan 30;20(1):e1011851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011851. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38289973 Free PMC article.
-
Ailanthone suppresses the activity of human colorectal cancer cells through the STAT3 signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Feb;49(2):21. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5076. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34958109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miura K, Satoh M, Kinouchi M, Yamamoto K, Hasegawa Y, Philchenkov A, Kakugawa Y, Fujiya T. Expert opinion on drug discovery. 2014;9:1087–1101. - PubMed
-
- Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C, Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC, Lynch DH. Nature medicine. 1999;5:157–163. - PubMed
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA, et al. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

