Capsaicin modulates acetylcholine release at the myoneural junction
- PMID: 25446918
- PMCID: PMC4261065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.09.044
Capsaicin modulates acetylcholine release at the myoneural junction
Abstract
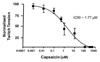
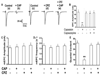
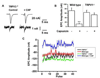
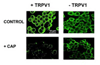
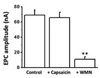
Transient receptor potential (TRP) proteins are non-selective cation channel proteins that are expressed throughout the body. Previous studies demonstrated the expression of TRP Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), capsaicin (CAP) receptor, in sensory neurons. Recently, we reported TRPV1 expression in mouse motor nerve terminals [MNTs; (Thyagarajan et al., 2009)], where we observed that CAP protected MNTs from botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A). Phrenic nerve diaphragm nerve muscle preparations (NMP) isolated from isoflurane anesthetized adult mice were analyzed for twitch tension, spontaneous (mEPCs) and nerve stimulus evoked (EPCs) acetylcholine release. When acutely applied to isolated NMP, CAP produced a concentration-dependent decline of twitch tension and produced a significant decline in the amplitude of EPCs and quantal content without any effect on the mEPCs. The suppression of nerve stimulus evoked acetylcholine release by CAP was antagonized by capsazepine (CPZ), a TRPV1 antagonist. CAP did not suppress phrenic nerve stimulus evoked acetylcholine release in TRPV1 knockout mice. Also, CAP treatment, in vitro, interfered with the localization of adapter protein 2 in cholinergic Neuro 2a cells. Wortmannin, (WMN; non-selective phosphoinositol kinase inhibitor), mimicked the effects of CAP by inhibiting the acetylcholine exocytosis. Our data suggest that TRPV1 proteins expressed at the MNT are coupled to the exo-endocytic mechanisms to regulate neuromuscular functions.
Keywords: Acetylcholine release; Capsaicin; Capsaicin (PubChem CID: 1548943); Endocytosis; Exocytosis; Motor nerve terminal; Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PubChem CID: 5311358GTPL2387); TRPV1; capsazepine (PubChem CID: 2733484.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

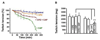

Similar articles
-
Capsaicin protects mouse neuromuscular junctions from the neuroparalytic effects of botulinum neurotoxin a.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Nov;331(2):361-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.156901. Epub 2009 Aug 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19654265 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and chronic effects of botulinum neurotoxin a on the mammalian neuromuscular junction.Muscle Nerve. 2014 Aug;50(2):206-15. doi: 10.1002/mus.24119. Epub 2014 May 9. Muscle Nerve. 2014. PMID: 24218344
-
Opposing effects of cannabinoids and vanilloids on evoked quantal release at the frog neuromuscular junction.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Apr 5;473(2):97-101. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.02.026. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20176082
-
Activation of TRPV1 Channels Inhibits the Release of Acetylcholine and Improves Muscle Contractility in Mice.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):4157-4172. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01403-y. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37689594 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin, the primary constituent of pepper sprays and its pharmacological effects on mammalian ocular tissues.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 15;819:114-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.042. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29191767 Review.
Cited by
-
Kainic Acid Activates TRPV1 via a Phospholipase C/PIP2-Dependent Mechanism in Vitro.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Oct 7;11(19):2999-3007. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00297. Epub 2020 Sep 11. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32833423 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-low doses of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 agonist, resiniferatoxin, prevents vomiting evoked by diverse emetogens in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva).Behav Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;31(1):3-14. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000499. Behav Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31503071 Free PMC article.
-
Dscam2 suppresses synaptic strength through a PI3K-dependent endosomal pathway.J Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 1;219(6):e201909143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201909143. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32259198 Free PMC article.
-
Ingestion of transient receptor potential channel agonists attenuates exercise-induced muscle cramps.Muscle Nerve. 2017 Sep;56(3):379-385. doi: 10.1002/mus.25611. Epub 2017 May 9. Muscle Nerve. 2017. PMID: 28192854 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant Analogs of Sea Anemone Kunitz-Type Peptides Influence P2X7 Receptor Activity in Neuro-2a Cells.Mar Drugs. 2023 Mar 20;21(3):192. doi: 10.3390/md21030192. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anas A, Okuda T, Kawashima N, Nakayama K, Itoh T, Ishikawa M, Biju V. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of quantum dot-peptide conjugates in living cells. ACS Nano. 2009;3:2419–2429. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Julius D. The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D. The CAP receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature. 1997;389:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Cui JG, Zhang X, Zhao YH, Chen C, Bazan N. Allodynia and hyperalgesia suppression by a novel analgesic in experimental neuropathic pain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;350:358–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

