Method for measuring lipid mediators, proteins, and messenger RNAs from a single tissue specimen
- PMID: 25447462
- PMCID: PMC4257868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.10.004
Method for measuring lipid mediators, proteins, and messenger RNAs from a single tissue specimen
Abstract
This article describes a new method for extracting RNA, protein, and lipid mediators from a single tissue specimen. Specifically, mouse bone fracture callus specimens were extracted into a single solution that was processed using three different procedures to measure messenger RNA (mRNA) levels by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RTqPCR), cytokines and growth factors using an xMAP method, and lipid mediators by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). This method has several advantages because it decreases the number of animals necessary for experimentation, allows division of the sample from a homogeneous mixture that reduces sample variability, and uses a solution that protects the integrity of the macromolecules during storage.
Keywords: Bone regeneration; Fracture healing; Lipid mediator; Metabolomics.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
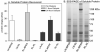


Similar articles
-
Variation in lipid mediator and cytokine levels during mouse femur fracture healing.J Orthop Res. 2016 Nov;34(11):1883-1893. doi: 10.1002/jor.23213. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Orthop Res. 2016. PMID: 26919197
-
Identification of estrogen-regulated genes during fracture healing, using DNA microarray.J Bone Miner Metab. 2004;22(3):224-35. doi: 10.1007/s00774-003-0482-y. J Bone Miner Metab. 2004. PMID: 15108064
-
Comprehensive quantitative determination of PUFA-related bioactive lipids for functional lipidomics using high-resolution mass spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1198:221-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1258-2_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25270932
-
Can bisphosphonates be given to patients with fractures?J Bone Miner Res. 2001 Mar;16(3):437-40. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.3.437. J Bone Miner Res. 2001. PMID: 11277260 Review. No abstract available.
-
A review of analytical methods for eicosanoids in brain tissue.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Aug 1;964:50-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 14. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24685838 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid droplets and lipid mediators in viral infection and immunity.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2021 Aug 17;45(4):fuaa066. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa066. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33512504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired fracture healing is associated with callus chondro-osseous junction abnormalities in periostin-null and osteopontin-null mice.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025 Jan 22;249:10066. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2024.10066. eCollection 2024. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025. PMID: 39911634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Claes L, Recknagel S, Ignatius A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nature reviews. Rheumatology. 2012;8:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Gerstenfeld LC, Cullinane DM, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA. Fracture healing as a post-natal developmental process: molecular, spatial, and temporal aspects of its regulation. Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2003;88:873–884. - PubMed
-
- Simon AM, Manigrasso MB, O'Connor JP. Cyclo-oxygenase 2 function is essential for bone fracture healing. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2002;17:963–976. - PubMed
-
- Simon AM, O'Connor JP. Dose and time-dependent effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on fracture-healing. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2007;89:500–511. - PubMed
-
- Cottrell JA, O'Connor JP. Pharmacological inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase accelerates and enhances fracture-healing. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2009;91:2653–2665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

