Dual targeting of the thioredoxin and glutathione antioxidant systems in malignant B cells: a novel synergistic therapeutic approach
- PMID: 25448488
- PMCID: PMC4324472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2014.10.004
Dual targeting of the thioredoxin and glutathione antioxidant systems in malignant B cells: a novel synergistic therapeutic approach
Abstract
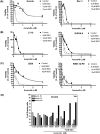
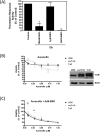
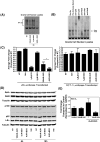
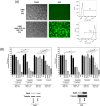
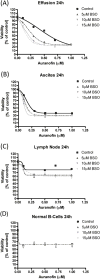
B-cell malignancies are a common type of cancer. One approach to cancer therapy is to either increase oxidative stress or inhibit the stress response systems on which cancer cells rely. In this study, we combined nontoxic concentrations of Auranofin (AUR), an inhibitor of the thioredoxin system, with nontoxic concentrations of buthionine-sulfoximine (BSO), a compound that reduces intracellular glutathione levels, and investigated the effect of this drug combination on multiple pathways critical for malignant B-cell survival. Auranofin interacted synergistically with BSO at low concentrations to trigger death in multiple malignant B-cell lines and primary mantle-cell lymphoma cells. Additionally, there was less toxicity toward normal B cells. Low AUR concentrations inhibited thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) activity, an effect significantly increased by BSO cotreatment. Overexpression of TrxR partially reversed AUR+BSO toxicity. Interestingly, the combination of AUR+BSO inhibited nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling. Moreover, synergistic cell death induced by this regimen was attenuated in cells overexpressing NF-κB proteins, arguing for a functional role for NF-κB inhibition in AUR+BSO-mediated cell death. Together, these findings suggest that AUR+BSO synergistically induces malignant B-cell death, a process mediated by dual inhibition of TrxR and NF-κB, and such an approach warrants further investigation in B-cell malignancies.
Copyright © 2015 ISEH - International Society for Experimental Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sharma SV, Settleman J. Exploiting the balance between life and death: targeted cancer therapy and “oncogenic shock”. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80:666–673. - PubMed
-
- Champion GD, Cairns DR, Bieri D, et al. Dose response studies and longterm evaluation of auranofin in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:28–34. - PubMed
-
- Williams HJ, Ward JR, Egger MJ, et al. Auranofin, gold sodium thiomalate, and placebo in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Cooperative systematic studies of rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 1984;3(Suppl 1):39–50. - PubMed
-
- Furst DE. Mechanism of action, pharmacology, clinical efficacy and side effects of auranofin. An orally administered organic gold compound for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacotherapy. 1983;3:284–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

