Increased serum tumor necrosis factor α levels in patients with lenalidomide-induced hypothyroidism
- PMID: 25448491
- PMCID: PMC5002942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2014.10.009
Increased serum tumor necrosis factor α levels in patients with lenalidomide-induced hypothyroidism
Abstract
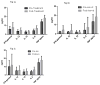
As the use of lenalidomide expands, the poorly understood phenomenon of lenalidomide-induced thyroid abnormalities will increase. In this study, we compared rates of therapy-induced hypothyroidism in 329 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treated with conventional chemotherapy (DLBCL-c) or conventional chemotherapy plus lenalidomide (DLBCL-len). We measured serum levels of tumor necrosis factor α, interferon gamma, interleukin 6, interleukin 12, and interleukin 15 before and after treatment. We found a significantly higher rate of therapy-induced hypothyroidism in the DLBCL-len group (25.8% vs. 1.3%), and we found a statistically significant increase in serum tumor necrosis factor α in patients with lenalidomide-induced hypothyroidism.
Copyright © 2015 ISEH - International Society for Experimental Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflict of Interest: NMR; advisory board and research funding: Celgene
Figures

References
-
- Wiernik PH, Lossos IS, Tuscano JM, et al. Lenalidomide monotherapy in relapsed or refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4952–4957. - PubMed
-
- Witzig TE, Vose JM, Zinzani PL, et al. An international phase II trial of single-agent lenalidomide for relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1622–1627. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Deeb G, Zinzani PL, et al. Higher response to lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in nongerminal center B-cell-like than in germinal center B-cell-like phenotype. Cancer. 2011;117:5058–5066. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Fowler N, Wagner-Bartak N, et al. Oral lenalidomide with rituximab in relapsed or refractory diffuse large cell, follicular and transformed lymphoma: a phase II clinical trial. Leukemia. 2013;27:1902–1909. - PubMed
-
- Zinzani PL, Pellegrini C, Gandolfi L, et al. Combination of lenalidomide and rituximab in elderly patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a phase 2 trial. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011;11:462–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

