Reading and phonological skills in boys with fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 25448919
- PMCID: PMC4442735
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-014-2328-y
Reading and phonological skills in boys with fragile X syndrome
Abstract
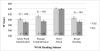
Although reading skills are critical for the success of individuals with intellectual disabilities, literacy has received little attention in fragile X syndrome (FXS). This study examined the literacy profile of FXS. Boys with FXS (n = 51; mean age 10.2 years) and mental age-matched boys with typical development (n = 35) participated in standardized assessments of reading and phonological skills. Phonological skills were impaired in FXS, while reading was on-par with that of controls. Phonological awareness predicted reading ability and ASD severity predicted poorer phonological abilities in FXS. Boys with FXS are capable of attaining reading skills that are commensurate with developmental level and phonological awareness skills may play a critical role in reading achievement in FXS.
Figures
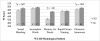
Similar articles
-
Reading in Children With Fragile X Syndrome: Phonological Awareness and Feasibility of Intervention.Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018 May;123(3):193-211. doi: 10.1352/1944-7558-123.3.193. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018. PMID: 29671637 Free PMC article.
-
Phonological awareness and reading in boys with fragile X syndrome.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2015 Jan;56(1):30-9. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12267. Epub 2014 Jun 3. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24889646 Free PMC article.
-
Grammar in Boys With Idiopathic Autism Spectrum Disorder and Boys With Fragile X Syndrome Plus Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018 Apr 17;61(4):857-869. doi: 10.1044/2017_JSLHR-L-17-0248. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 29541769 Free PMC article.
-
Autism Symptoms in Fragile X Syndrome.J Child Neurol. 2017 Sep;32(10):903-909. doi: 10.1177/0883073817712875. Epub 2017 Jun 15. J Child Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28617074 Review.
-
Melatonin as a Novel Interventional Candidate for Fragile X Syndrome with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 20;18(6):1314. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061314. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28632163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reading in Children With Fragile X Syndrome: Phonological Awareness and Feasibility of Intervention.Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018 May;123(3):193-211. doi: 10.1352/1944-7558-123.3.193. Am J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2018. PMID: 29671637 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Autism Co-Occurrence in Fragile X Syndrome: Proposing a Preliminary CARS-2 Cut-Off Score.J Autism Dev Disord. 2025 May 21:10.1007/s10803-025-06888-8. doi: 10.1007/s10803-025-06888-8. Online ahead of print. J Autism Dev Disord. 2025. PMID: 40397047 Free PMC article.
-
Gesture Frequency and Function in Infants With Fragile X Syndrome and Infant Siblings of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2019 Jul 15;62(7):2386-2399. doi: 10.1044/2019_JSLHR-L-17-0491. Epub 2019 Jun 27. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2019. PMID: 31251678 Free PMC article.
-
Rates and Predictors of Co-occurring Autism Spectrum Disorder in Boys with Fragile X Syndrome.Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2020 Jan-Dec;5:2396941520905328. doi: 10.1177/2396941520905328. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2020. PMID: 35847766 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of the Hebb-Williams Maze Paradigm for Translational Research in Fragile X Syndrome: A Direct Comparison of Mice and Humans.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Mar 28;11:99. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00099. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29643767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbeduto L, Hagerman RJ. Language and communication in fragile X syndrome. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 1997;3(4):313–322.
-
- Adams MJ. Learning to read: Thinking and learning about print. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1990.
-
- Bailey DB, Raspa M, Holiday D, Bishop E, Olmsted M. Functional skills of individuals with fragile x syndrome: a lifespan cross-sectional analysis. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. 2009;114(4):289–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

