Integrated genomic analyses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- PMID: 25449221
- PMCID: PMC4344889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.09.052
Integrated genomic analyses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Abstract
Objective: To identify single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and pathways associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) because O2 requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age risk is strongly influenced by heritable factors.
Study design: A genome-wide scan was conducted on 1.2 million genotyped SNPs, and an additional 7 million imputed SNPs, using a DNA repository of extremely low birth weight infants. Genome-wide association and gene set analysis was performed for BPD or death, severe BPD or death, and severe BPD in survivors. Specific targets were validated via the use of gene expression in BPD lung tissue and in mouse models.
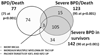
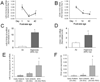
Results: Of 751 infants analyzed, 428 developed BPD or died. No SNPs achieved genome-wide significance (P < 10(-8)), although multiple SNPs in adenosine deaminase, CD44, and other genes were just below P < 10(-6). Of approximately 8000 pathways, 75 were significant at false discovery rate (FDR) <0.1 and P < .001 for BPD/death, 95 for severe BPD/death, and 90 for severe BPD in survivors. The pathway with lowest FDR was miR-219 targets (P = 1.41E-08, FDR 9.5E-05) for BPD/death and phosphorous oxygen lyase activity (includes adenylate and guanylate cyclases) for both severe BPD/death (P = 5.68E-08, FDR 0.00019) and severe BPD in survivors (P = 3.91E-08, FDR 0.00013). Gene expression analysis confirmed significantly increased miR-219 and CD44 in BPD.
Conclusions: Pathway analyses confirmed involvement of known pathways of lung development and repair (CD44, phosphorus oxygen lyase activity) and indicated novel molecules and pathways (adenosine deaminase, targets of miR-219) involved in genetic predisposition to BPD.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: another step along the path.J Pediatr. 2015 Mar;166(3):521-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.11.028. Epub 2014 Dec 30. J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25556019 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bhandari V, Bizzarro MJ, Shetty A, Zhong X, Page GP, Zhang H, et al. Familial and genetic susceptibility to major neonatal morbidities in preterm twins. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1901–1906. - PubMed
-
- Weber B, Borkhardt A, Stoll-Becker S, Reiss I, Gortner L. Polymorphisms of surfactant protein A genes and the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants. Turk J Pediatr. 2000;42:181–185. - PubMed
-
- Rova M, Haataja R, Marttila R, Ollikainen V, Tammela O, Hallman M. Data mining and multiparameter analysis of lung surfactant protein genes in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:1095–1104. - PubMed
-
- Lin HC, Su BH, Chang JS, Hsu CM, Tsai CH, Tsai FJ. Nonassociation of interleukin 4 intron 3 and 590 promoter polymorphisms with bronchopulmonary dysplasia for ventilated preterm infants. Biol Neonate. 2005;87:181–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR6022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR7122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR30/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG4423/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21415/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004423/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27881/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

