The leucine-rich amelogenin protein (LRAP) is primarily monomeric and unstructured in physiological solution
- PMID: 25449314
- PMCID: PMC4400868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2014.10.007
The leucine-rich amelogenin protein (LRAP) is primarily monomeric and unstructured in physiological solution
Abstract
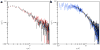
Amelogenin proteins are critical to the formation of enamel in teeth and may have roles in controlling growth and regulating microstructures of the intricately woven hydroxyapatite (HAP). Leucine-rich amelogenin protein (LRAP) is a 59-residue splice variant of amelogenin and contains the N- and C-terminal charged regions of the full-length protein thought to control crystal growth. Although the quaternary structure of full-length amelogenin in solution has been well studied and can consist of self-assemblies of monomers called nanospheres, there is limited information on the quaternary structure of LRAP. Here, sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation (SV) and small angle neutron scattering (SANS) were used to study the tertiary and quaternary structure of LRAP at various pH values, ionic strengths, and concentrations. We found that the monomer is the dominant species of phosphorylated LRAP (LRAP(+P)) over a range of solution conditions (pH 2.7-4.1, pH 4.5-8, 50 mmol/L(mM) to 200 mM NaCl, 0.065-2 mg/mL). The monomer is also the dominant species for unphosphorylated LRAP (LRAP(-P)) at pH 7.4 and for LRAP(+P) in the presence of 2.5 mM calcium at pH 7.4. LRAP aggregates in a narrow pH range near the isoelectric point of pH 4.1. SV and SANS show that the LRAP monomer has a radius of ∼2.0 nm and an asymmetric structure, and solution NMR studies indicate that the monomer is largely unstructured. This work provides new insights into the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of LRAP in solution and provides evidence that the monomeric species may be an important functional form of some amelogenins.
Keywords: Amelogenin; Biomineralization; Enamel; LRAP; Nanosphere.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




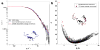

Similar articles
-
Neutron reflectometry studies of the adsorbed structure of the amelogenin, LRAP.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Mar 21;117(11):3098-109. doi: 10.1021/jp311936j. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23477285 Free PMC article.
-
A solution NMR investigation into the murine amelogenin splice-variant LRAP (Leucine-Rich Amelogenin Protein).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Sep;1804(9):1768-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.03.006. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20304108 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation and ionic strength alter the LRAP-HAP interface in the N-terminus.Biochemistry. 2013 Apr 2;52(13):2196-205. doi: 10.1021/bi400071a. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23477367 Free PMC article.
-
Controls of nature: Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of the enamel protein amelogenin in solution and on hydroxyapatite.J Struct Biol. 2020 Dec 1;212(3):107630. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2020.107630. Epub 2020 Sep 24. J Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32979496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in amelogenin biochemistry.Connect Tissue Res. 1995;32(1-4):119-24. doi: 10.3109/03008209509013713. Connect Tissue Res. 1995. PMID: 7554907 Review.
Cited by
-
Physicochemical understanding of biomineralization by molecular vibrational spectroscopy: From mechanism to nature.Exploration (Beijing). 2023 Jul 26;3(6):20230033. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20230033. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exploration (Beijing). 2023. PMID: 38264681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembly and mineralization of full-length human amelogenin and its functional fragments in vitro.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 1;39(4):419-424. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.04.007. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34409797 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
SAXS of murine amelogenin identifies a persistent dimeric species from pH 5.0 to 8.0.J Struct Biol. 2024 Dec;216(4):108131. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2024.108131. Epub 2024 Oct 4. J Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 39368677
-
Amelogenin is a Potential Biomarker for the Aggressiveness in Odontogenic Tumors.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 May 26;19(5):1375-1379. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.5.1375. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29802703 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of major matrix metalloproteinase-20 proteolytic processing products of murine amelogenin and tyrosine-rich amelogenin peptide using a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy based method.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 Sep;93:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 29960917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin HD, Olsen I, Knowles JC, Donos N. Differential Effect of Amelogenin Peptides on Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro: Identification of Possible New Drugs for Bone Repair and Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18:1193–1202. - PubMed
-
- Boabaid F, Gibson CW, Kuehl MA, Berry JE, Snead ML, Nociti FHJ, Katchburian E, Somerman MJ. Leucine-rich amelogenin peptide: a candidate signaling molecule during cementogenesis. J Periodontol. 2004;75:1126–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

